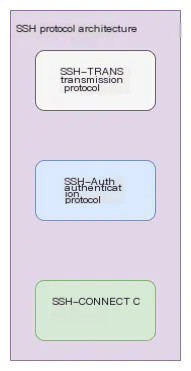
The SSH protocol is a protocol for remote secure login built on top of an insecure network. It is a suite of protocols that includes three sub-protocols, which are:
- 1. Transport layer protocol
[SSH-TRANS]: Provides server authentication, integrity, and confidentiality, and is built on top of the traditional TCP/IP protocol. - 2. Authentication protocol
[SSH-USERAUTH]: Authenticates the client user to the server, with username-password and public-key based authentication methods, built on top of the transport layer protocol[SSH-TRANS]. - 3. Connection protocol
[SSH-CONNECT]: Multiplexes the encrypted tunnel into several logical channels. It is built on top of the authentication protocol.
 />
/>
Before continuing, let’s supplement with two concepts:
- 1.
Session key: The key is negotiated between the client and server through algorithms such as D-H. - 2.
Public key: The public key becomes theserver_host_key, used for server authentication in theSSH-TRANStransport protocol. It’s essentially used by the client to verify the server.
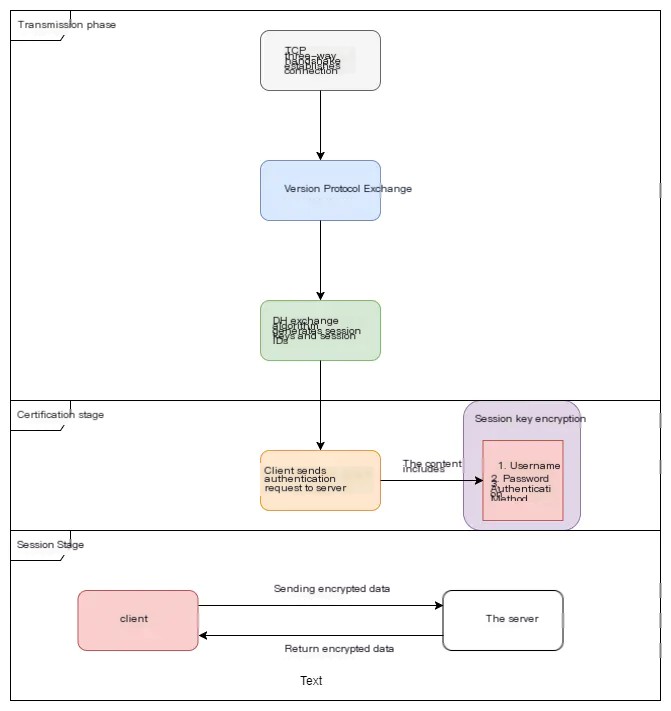
The overall process of the SSH protocol handshake is shown as follows:
 />
/>
The following uses Wireshark for packet capture analysis, start capturing with Wireshark, perform a normal SSH login, stop capturing, filter out relevant packets through IP as follows:
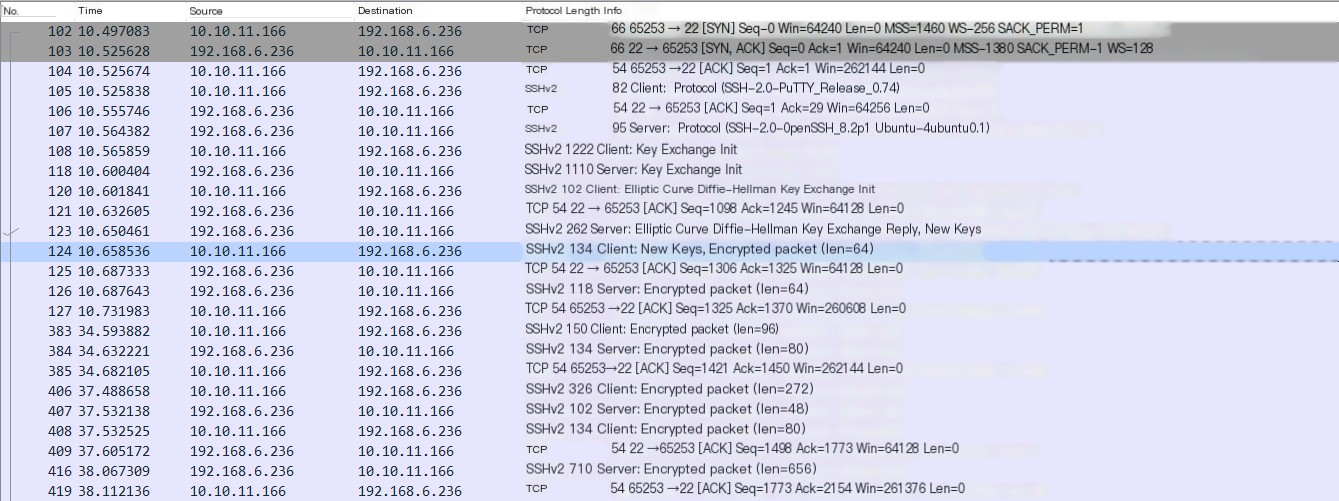
If the above packets are analyzed following the SSH protocol operation process, the correspondence between the process and the packets is as follows:
- TCP three-way handshake

- Version protocol exchange

- Key exchange
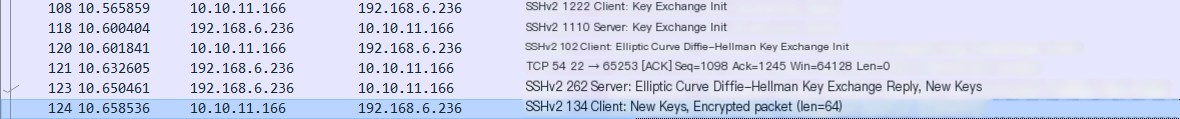
During the negotiation stage, the client and server notify each other of the encryption methods they support:
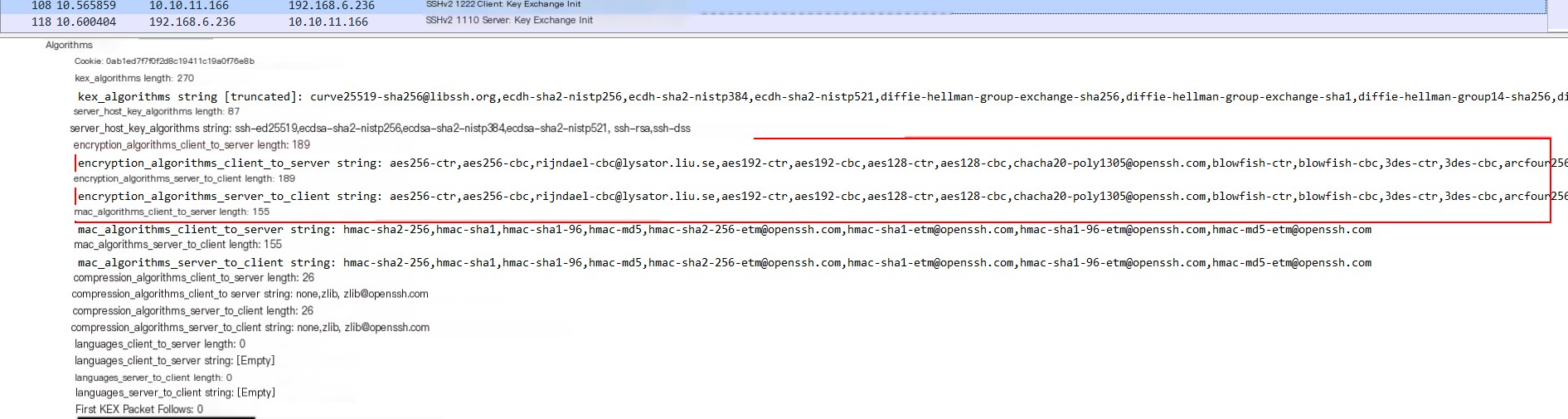
Once encryption methods are determined, public keys are exchanged:
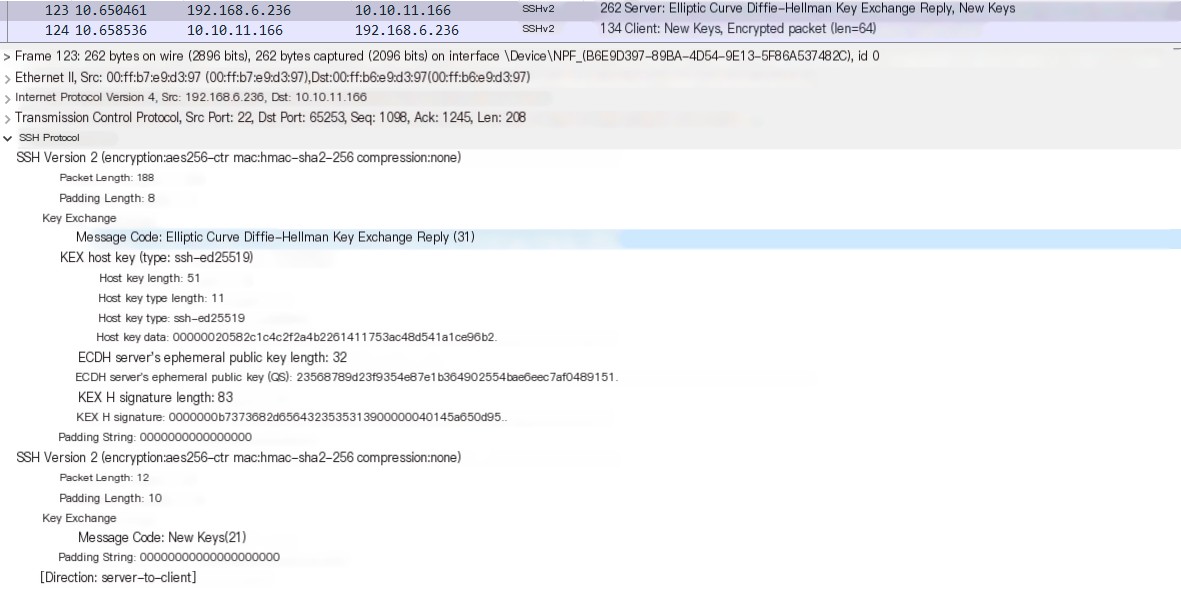
- Encrypted communication
If logging in with a password, SSH will use this automatically negotiated key for asymmetric encrypted communication. From then on, the packets are encrypted.
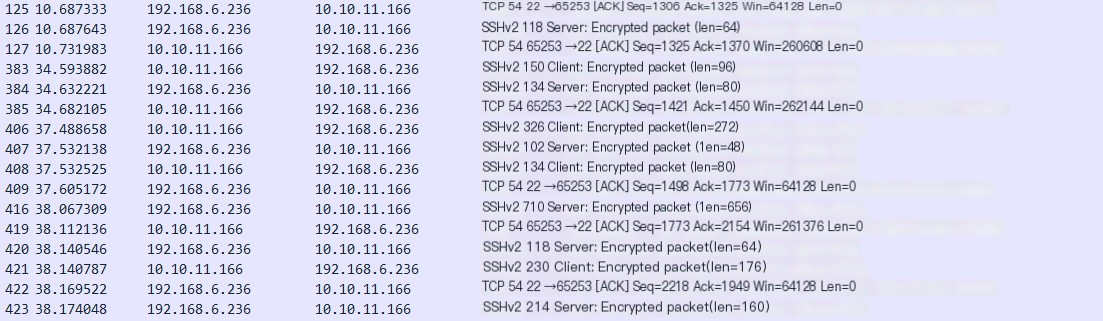
Essentially, New Keys acts as a boundary, distinguishing key negotiation from encrypted communication.
What exactly is the principle of internal encryption? This requires further exploration.