DNS Message Format
The DNS message format is crucial in the process of domain name resolution. It defines the structure
 />
/>
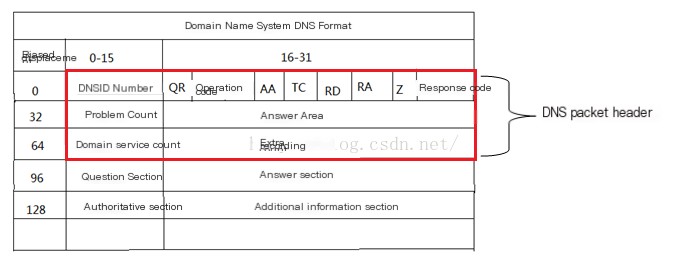
The image above shows the DNS message format, which is divided into five main sections. These are: Header, Question Section, Answer Section, Authority Section, and Additional Information Section. However, not all five sections are required; only the Header is mandatory, while other sections may not be present in certain cases.
Let’s first look at the meaning of each field in the Header section:
DNS ID Number: Used to match DNS queries with DNS responses
Query/Response (QR): Indicates whether the message is a DNS query or response, occupying 1 bit. 1 represents a response, 0 represents a query
Operation Code (OpCode): Used to define the type of request in the message
Authoritative Answer (AA): This bit is meaningful only in responses, indicating that the response is from an authoritative domain name server
Truncation (TC): Indicates that the message is longer than the allowed length, resulting in truncation
Recursion Desired (RD): If set, suggests that the domain name server should perform recursive resolution, and support for recursive queries is optional.
Recursion Available (RA): When this value is set in the response, it indicates that the domain name server supports recursive queries
Reserved (Z): Unused, represented by 0
Response Code: Indicates errors in DNS responses, occupying 4 bits.
Question Count: Number of question records in the Question Section
Answer Count: Number of answer records in the Answer Section
Name Server Count: Number of records in the Authority Section
Additional Records Count: Number of records in the Additional Information Section
Question Section: Contains one or more records sent to the DNS server
Answer Section: Contains one or more resource records used to answer queries
Authority Section: Contains resource records from authoritative domain name servers
Additional Information Section: Contains variable-sized resource records.
(2) Capture DNS Packets
Open Wireshark, capture data, then open a browser and enter the URL: www.baidu.com

It is clearly seen that Frame 18 is a DNS request frame, and Frame 19 is a DNS response frame
(3) Analyze DNS Request Frame, corresponding to Frame 18
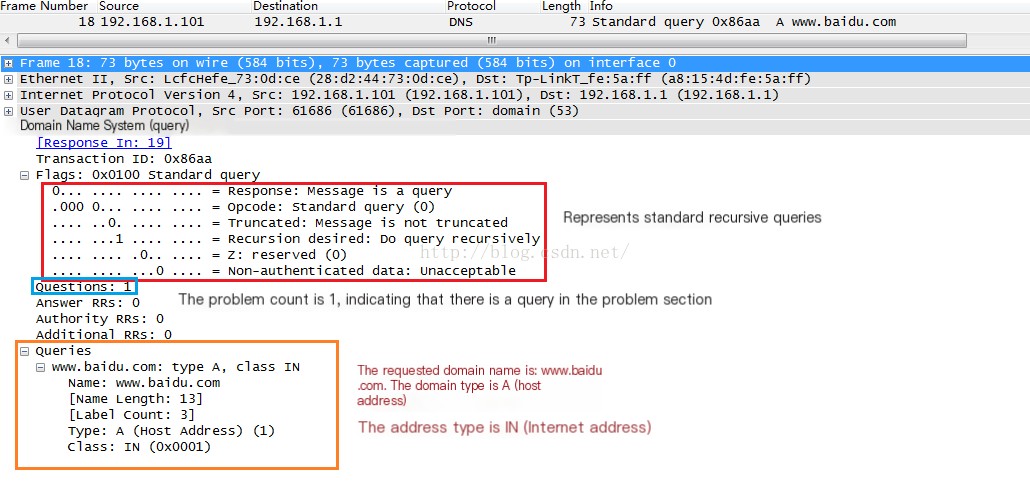
According to the analysis in the image above, the request count is 1, and the requested host domain name is www.baidu.com
(4) Analyze DNS Response Frame, corresponding to Frame 19
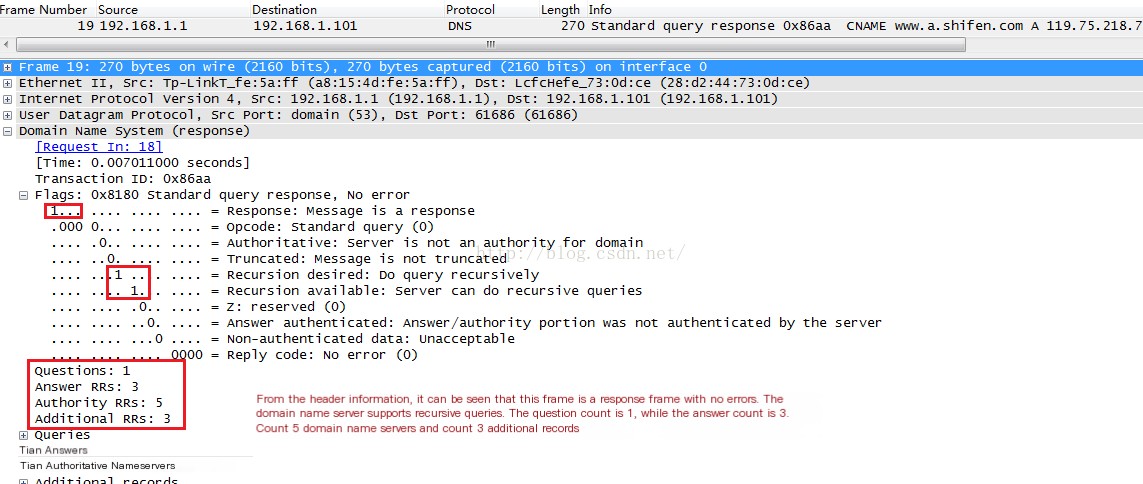
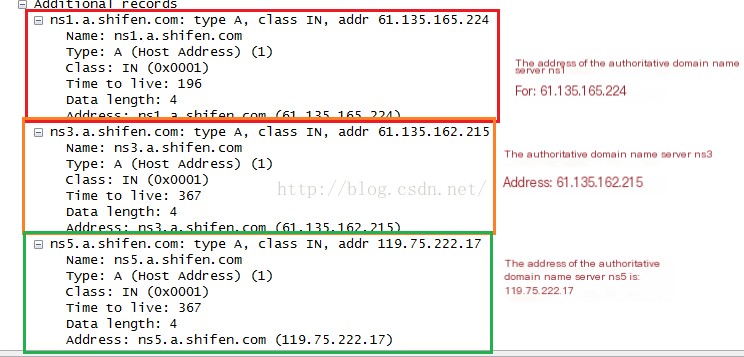
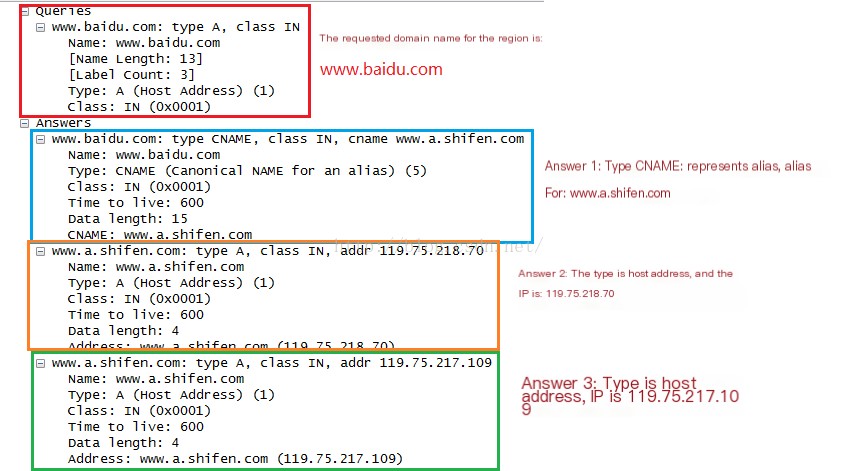
From the image above, it can be seen that there is 1 question count, corresponding to the question in the request frame. There are 3 response counts. Analyze the Answer field as follows
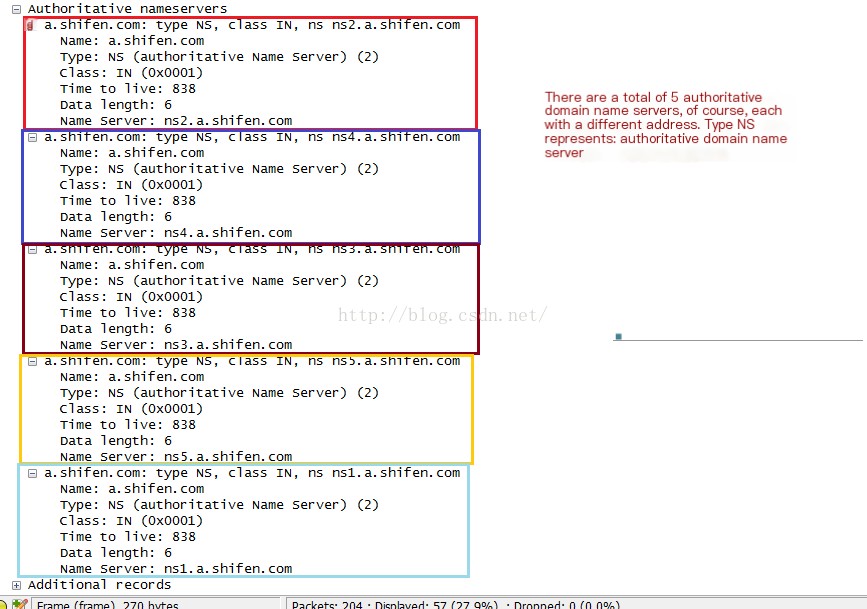
Analyze the Authority Section: This section contains authoritative domain name server resource records
Analyze the Additional Information Section: