Preface
A packet example from the Sharkfest Packet Challenge. Sharkfest is an annual conference organized by Wireshark, dedicated to sharing knowledge, experience, and best practices among Wireshark developers and user communities . I remember that it was held once a year in the early days, but in recent years it has become twice a year, one in the United States and one in other regions, such as Europe or Asia. Packet Challenge is one of the more interesting activities in the conference. Through a series of packet examples, participants can perform analysis challenges and test their comprehensive analysis capabilities.
Topic Information
This case is the second question Bad Address in the Sharkfest 2019 EU Packet Challenge , and the packet trace file is BadAddress.pcapng .
The main description is as follows:
Everybody wants an IP address…
1. How many unique non-broadcast MAC addresses can be found in the trace?
2. Why does the filter expression “ bootp ” give you a warning in Wireshark3.x and higher?
3. What is the IP address offered to the client?
4. Is the IP address accepted?
5. Why does the client keep requesting an IP address?
Packet information
The basic information of the packet trace file is as follows:
λ capinfos BadAddress.pcapng
File name: BadAddress.pcapng
File type: Wireshark/... - pcapng
File encapsulation: Ethernet
File timestamp precision: microseconds (6)
Packet size limit: file hdr: (not set)
Number of packets: 36
File size: 10 kB
Data size: 8869 bytes
Capture duration: 24.192910 seconds
First packet time: 2018-11-24 01:54:36.582252
Last packet time: 2018-11-24 01:55:00.775162
Data byte rate: 366 bytes/s
Data bit rate: 2932 bits/s
Average packet size: 246.36 bytes
Average packet rate: 1 packets/s
SHA256: a7b9dd06fc2ae3ec1df76bb67782ec8853130a6a01af9dcd8eecae480f3a9f25
RIPEMD160: 445dba317fa16d90a6430cdb68f59baa7eb56e7f
SHA1: 266f7a89d3887db47da585ac9bd87967c5d141c6
Strict time order: True
Capture application: Editcap (Wireshark) 3.0.6 (v3.0.6-0-g908c8e357d0f)
Number of interfaces in file: 1
Interface #0 info:
Encapsulation = Ethernet (1 - ether)
Capture length = 65535
Time precision = microseconds (6)
Time ticks per second = 1000000
Number of stat entries = 0
Number of packets = 36Captured by Wireshark, without truncation, the number of captured packets is 36, the capture duration is 24.19 seconds, the average rate is 2932 bps, and it has been edited by the Editcap tool.
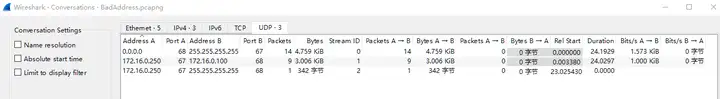
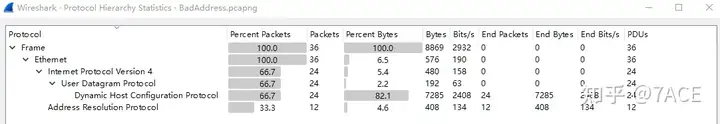
The session information and protocol information are shown below, including UDP session, broadcast traffic, and protocol information such as DHCP and ARP.
The expert information is as follows. You can see Warning level information Duplicate IP address configured, indicating that there is a conflicting IP problem.

Packet Analysis
Expand the data packet file information as follows, mainly DHCP and ARP packets.
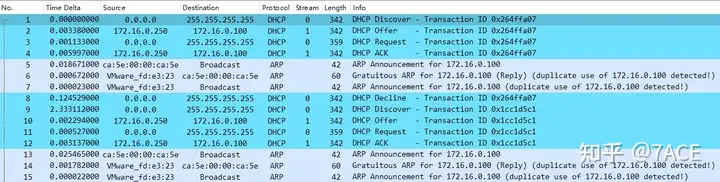
You can also view the type and number of DHCP messages through Statistics – DHCP(BOOTP) Information.
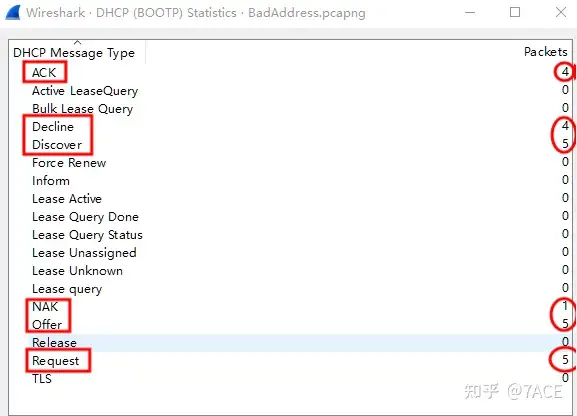
1. How many unique non-broadcast MAC addresses can be found in the trace?
How many unique non-broadcast MAC addresses can be found in the trace file ?
Analysis steps
Statistics – Endpoints information is as follows, showing the number of MAC addresses.
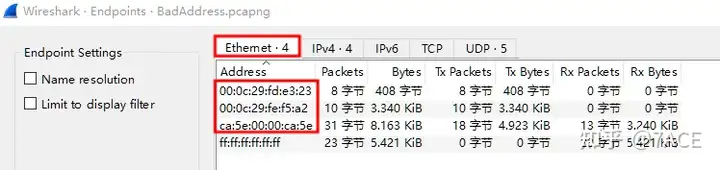
Analyze the answer
How many unique non-broadcast MAC addresses can be found in the trace file: 3.
2. Why does the filter expression “bootp” give you a warning in Wireshark 3.x and higher?
Why does the filter expression “bootp” give a warning in Wireshark 3.x and higher ?
Analysis steps
The filter expression bootpis displayed in yellow. Yellow generally means that the filter expression is accepted, but may not work as expected.
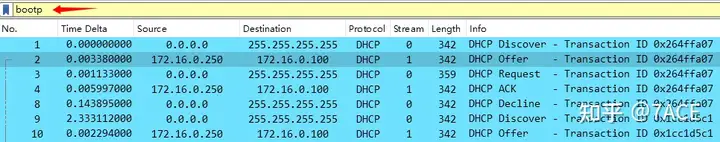
In fact, an explanation will be given in the status bar here, bootpwhich has been replaced.dhcp

6.4.8. Sometimes Fields Change NamesAs protocols evolve they sometimes change names or are superseded by newer standards. For example, DHCP extends and has largely replaced BOOTP and TLS has replaced SSL. If a
protocol dissector originally used the older names and fields for a protocol the Wireshark development team might update it to use the newer names and fields. In such cases they will add an alias from the old protocol name to the new one in order to make the transition easier. For example, the DHCP dissector was originally developed for the BOOTP protocol but as of Wireshark 3.0 all of the “bootp” display filter fields have been renamed to their “dhcp”
equivalents . You can still use the old filter names for the time being, eg, “bootp.type” is Equivalent to “dhcp.type” but Wireshark will show the warning “”bootp” is deprecated” when you use it. Support for the deprecated fields may be removed in the future.
The filter expression dhcpis displayed in green and the syntax is correct.
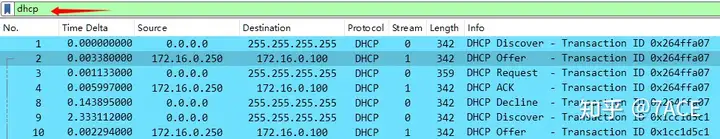
Analyze the answer
Why does the filter expression “bootp” give a warning in Wireshark 3.x and later? The bootp protocol has been updated to dhcp.
3. What is the IP address offered to the client?
What IP address is provided to the client ?
Analysis steps
DHCP OfferThe IP address information provided to the client can be viewed in the information.
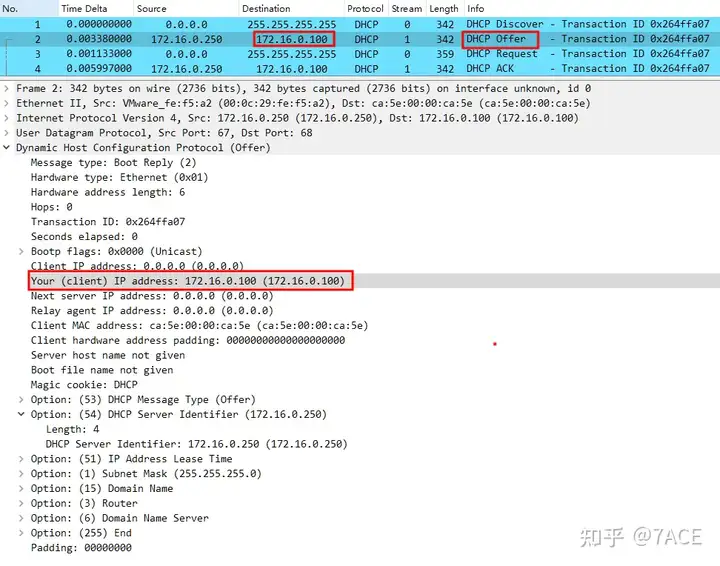
Analyze the answer
The IP address provided to the client is: 172.16.0.100.
4. Is the IP address accepted?
Is the IP address accepted?
Analysis steps
Those who are familiar with the DHCP principle process and messages will know that the client did not accept the IP address, and the reason is naturally the IP address conflict.
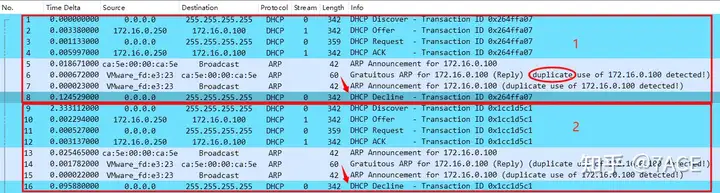
DHCP DECLINE : When the client finds that the IP address assigned by the server cannot be used (such as when there is an IP address conflict), it will send this message to notify the server to prohibit the use of the IP address.
Analyze the answer
Is the IP address accepted: Not accepted.
5. Why does the client keep requesting an IP address?
Why does the client keep requesting the IP address?
Analysis steps
This is the same as question 4. Because the IP address assigned by the DHCP server conflicts, the client does not accept the IP address and therefore continues to request it.
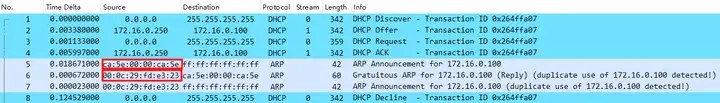
Client’s MAC address: ca:5e:00:00:ca:5e Conflicting IP’s MAC address: 00:0c:29:fd:e3:23
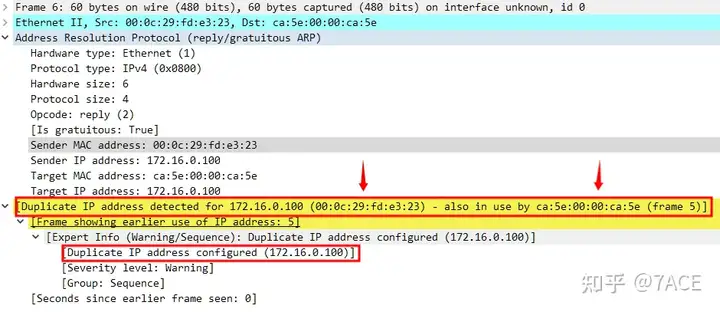
Analyze the answer
Why does the client keep requesting the IP address?: IP address conflict.