Apache HTTPD supports files with multiple suffixes and executes different directives for each suffix. For example, consider the following configuration file:
AddType text/html .html AddLanguage zh-CN .cn
Here, the `.html` suffix is assigned a media type with the value `text/html`, and the `.cn` suffix is assigned a language with the value `zh-CN`. At this point, if a user requests the file `index.cn.html`, it will return an HTML page in Chinese. This is the multi-suffix feature of Apache. If the system administrator adds a processor for the `.php` suffix:
AddHandler application/x-httpd-php .php
Then, in the case of multiple suffixes, any file containing the `.php` suffix will be recognized as a PHP file, regardless of whether it is the last suffix. Exploiting this feature can result in a parsing vulnerability that bypasses upload whitelists.
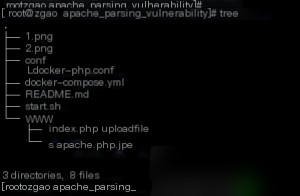
The vulnerability environment shows an incorrect PHP configuration file and demonstrates the vulnerable file.
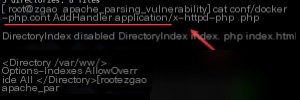
The issue lies here, where any file with a `.php` suffix is parsed as PHP. Let’s take a look at the `index.php` file, focusing on the file upload section of the code.
This provides a file upload feature, but it only checks the last suffix. Therefore, we can upload files with multiple suffixes as long as the last suffix meets the requirements. I won’t demonstrate the upload here; instead, I’ll use the provided file directly.
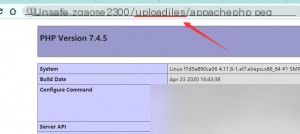
Since the filename contains the `.php` suffix, the incorrect configuration file causes it to be parsed and executed as PHP.
Vulnerability Mitigation (Reference from online methods)
1. Use `SetHandler` and write proper regular expressions:
SetHandler application/x-httpd-php
2. Disable execution of files like `.php`:


