What is Malware?
Malware (also: scumware), short for malicious software, is software designed to secretly access a computer system without the owner’s informed consent. The expression is a general term used by computer professionals to mean a variety of forms of hostile, intrusive, or annoying software or program code. The term “computer virus” is sometimes used as a catch-all phrase to include all types of malware, including true viruses.
Software is considered to be malware based on the perceived intent of the creator rather than any particular features. Malware includes computer viruses, worms, trojan horses, spyware, dishonest adware, scareware, crimeware, most rootkits, and other malicious and unwanted software or program. In law, malware is sometimes known as a computer contaminant, for instance in the legal codes of several U. S. states, including California and West Virginia.
How Does Malware Get Installed Onto Computers?
- Malware is downloaded
Malware can be downloaded to your computer through many different ways. The most prevalent way is by being bundled with apparently legitimate software. When the legitimate software is downloaded, the malware attaches itself to the “good” files. Another way malware can be downloaded is through false cookie and cache files that your Internet browser automatically downloads. - Malware Spreads
Once the malware downloads, it generally stays dormant until something triggers the malware to execute. These triggers can be as simple as runing a specific program or opening an Internet browser. Once the malware is triggered, it generally self-installs somewhere inside your computer’s invisible system files. Even if the malware was originally downloaded to a temporary cache folder, once it installs to the system folders, it will be impossible to remove. - Malware Infects Others
Many modern malware programs are able to harness the power of local Internet to spread to other computers.The most common way that malware spreads is through e-mail attachments. However, since e-mail virus scanners have become increasingly sensitive, malware has become less effective at spreading this way.
How to customize the security policy
First, we should analyze the object to be detected before customizing any security policy. We will take “Trojan IRCBot” as an example to introduce how to customize a security policy. “Trojan IRCBot” is the latest trojan to have been intercepted by us . Through the analysis of “Trojan IRCBot”, we found that the Trojan will send the HTTP request “http://http.icq.com.edgesuite.net/pub/ICQ_Win95_98_NT4/ICQ_4/Lite_Edition/icq4_setup.exe” to the remote host, that’s the significant feature of it. We can define security policy with this feature. It will be introduces as followings in detail:
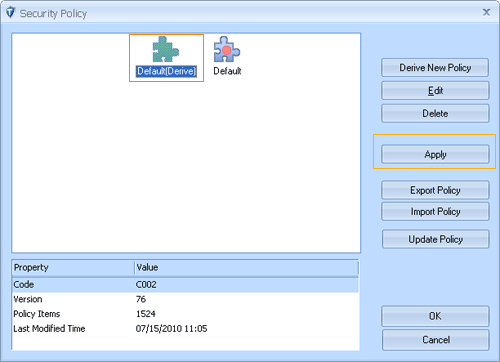
Step 1: click “Detection/ Policy” button ,Pop-up the “Security Policy” window. Select the policy settings which need to be modified (notice : Only a derived settings of policies that use the green icon to be identified can be modified)
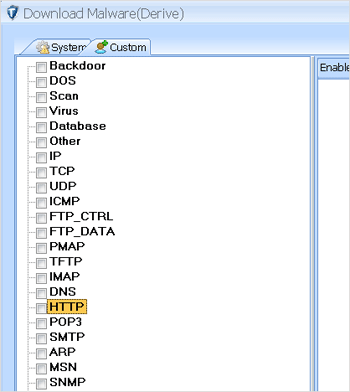
Step 2: Click “Edit” button, Pop-up the “Policy Maintenance” window, then switch “Custom” page. The whole window was divided by two parts., the left is a tree. According to different types ,all customized policies were listed. the corresponding details show on the right.
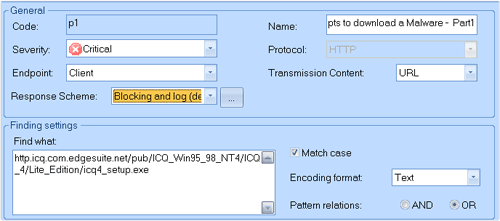
Step 3: Determine the type of policy. Such as “Trojan IRCBot “is adopted HTTP protocol ,so we choose “HTTP” on the left, then click “New” button at the bottom of window to add new policy, and select the new policy, the details settings of the policy will be displayed on the right window. As illustrated, we can set policy’s name , severity, endpoint, transmission content, find what and other information. We need to highlight that because the download request is sent to the server, so set Endpoint property as “Client”;
set the Transmission Content property as “URL”, Set the “Find what” as http.icq.com.edgesuite.net/pub/ICQ_Win95_98_NT4/ICQ_4/Lite_Edition/icq4_setup.exe. The three key settings show that we search “http.icq.com.edgesuite.net/pub/ICQ_Win95_98_NT4/ICQ_4/Lite_Edition/icq4_setup.exe” feature in the sent URLS, and then can set other auxiliary information.
Step 4: After the customizing of security policy, the new policy still not take effect automatically, so have to close the ” Policy Maintenance” window, then click “Apply” button and Re-load policy information to the detection engine.
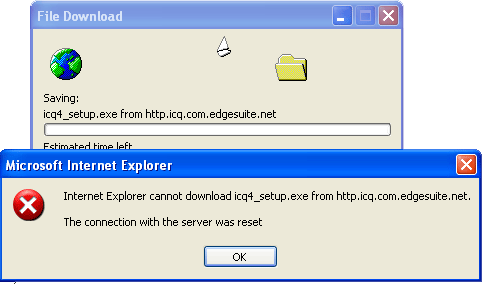
Step5: To test the policy, enter the http request “http://http.icq.com.edgesuite.net/pub/ICQ_Win95_98_NT4/ICQ_4/Lite_Edition/icq4_setup.exe” to browser, we will see that sax2 breaks the connection successfully.