While seeking refuge in Mexico, Mr. X remotely infiltrated the subnet of the Arctic Nuclear Fusion Research Facility (ANFRF) via the Internet. From within the facility (through a compromised system), he conducted some noisy network reconnaissance. Unfortunately for Mr. X, he wasn’t very discreet. Unluckily for Mr. X, the lab network was equipped to capture all traffic (including full content), and his activities were discovered and analyzed by you!As a network forensic investigator, your task is to answer the following questions:1. What is the IP address of Mr. X’s scanner?2. What type of port scan did Mr. X perform first? (Note: The scan includes thousands of packets), pick one:
3. What is the IP address of the target found by Mr. X?4. What is the MAC address of the Apple system he found?5. What is the IP address of the Windows system he found?6. Which TCP ports are open on the Windows system? (List the numbers from lowest to highest in decimal)
Packet Download:https://forensicscontest.com/contest04/evidence04.pcapAnalysis Process:First, open the packet with Wireshark, then try a simple port scan filter attempt:
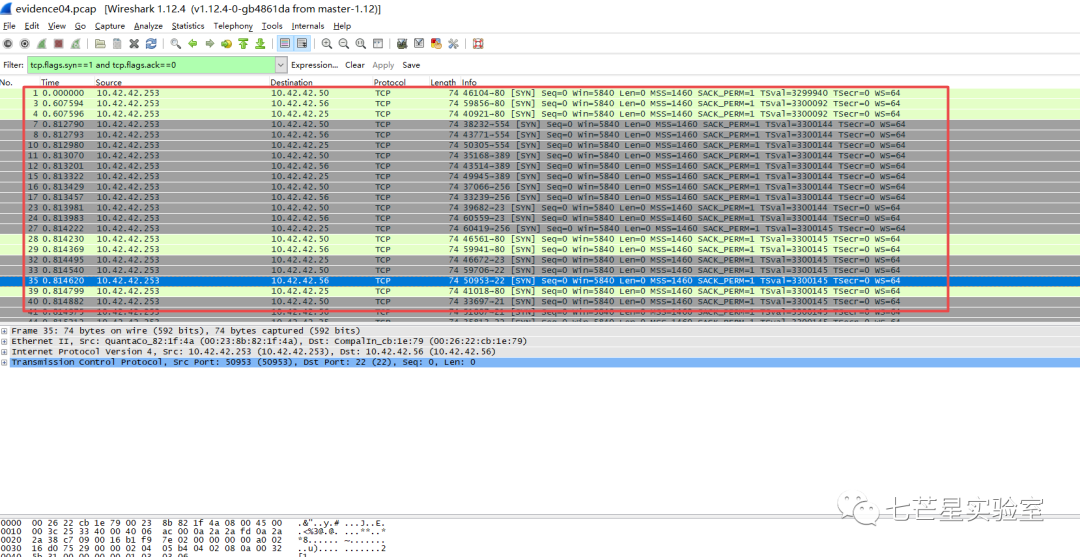
At this point, we can answer the first and second questions:
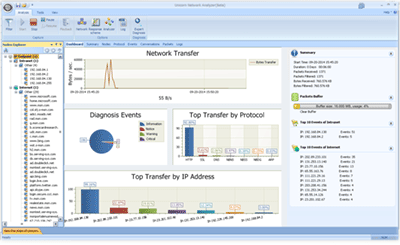
Since port scanning sends a large number of packets, we can look at Wireshark’s static-Endpoint to see which communication has the most traffic, indicating the scan packets.
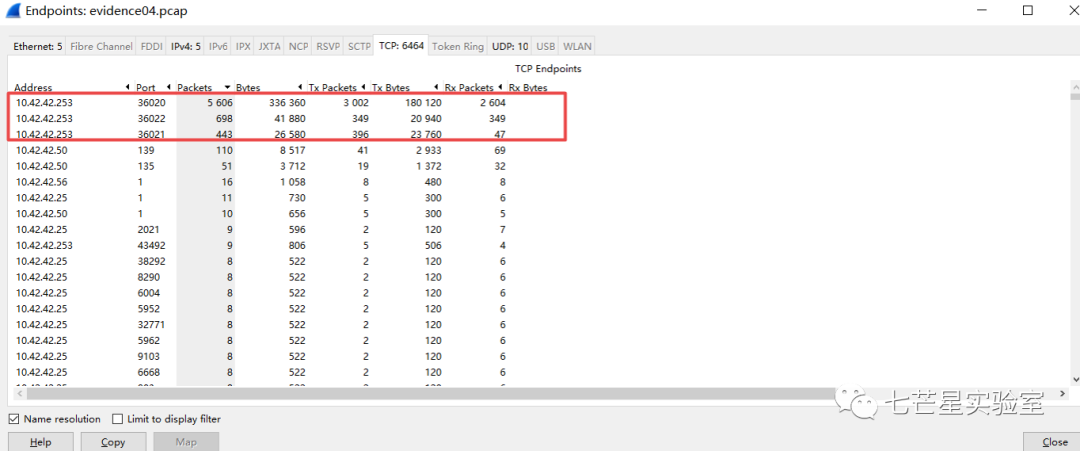
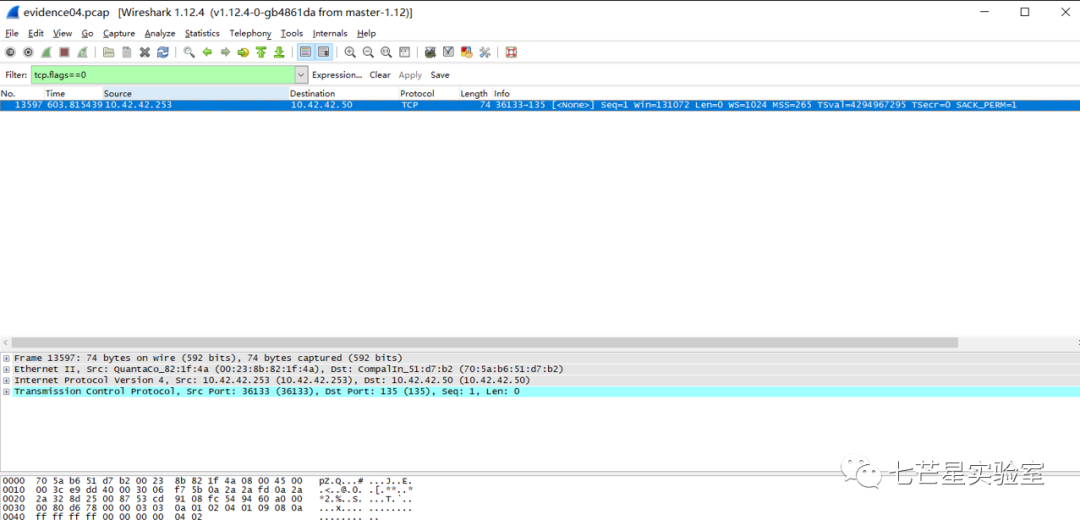
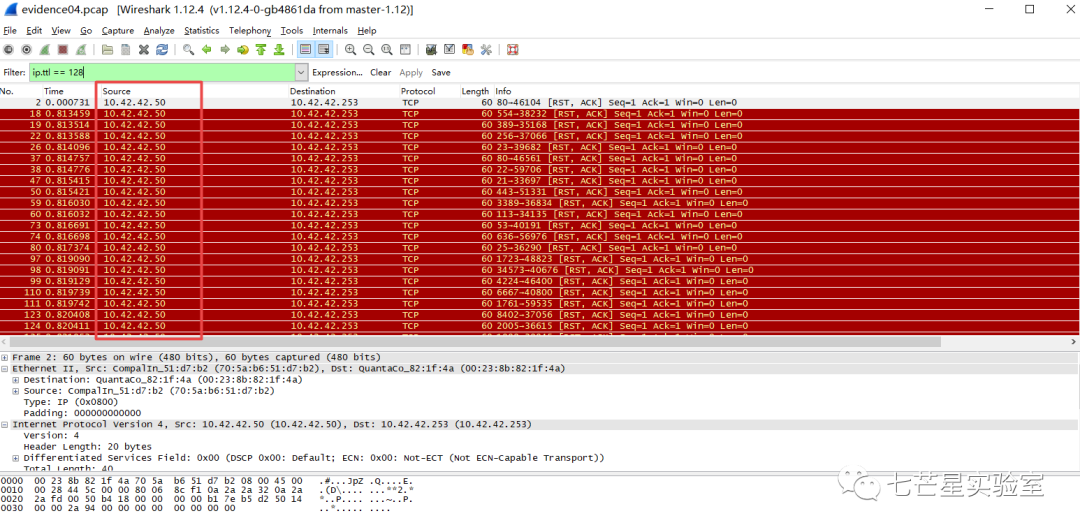
Next, we address the third question—”What is the IP address of the target found by Mr. X?” This question essentially asks us to identify the IP address of the live host detected by the attacker through port scanning. We can simply search for packets with an ack flag.
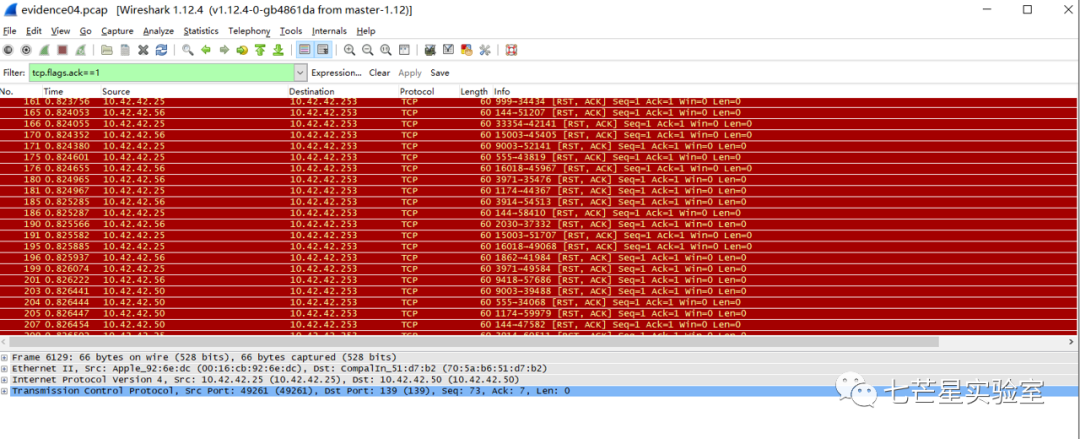
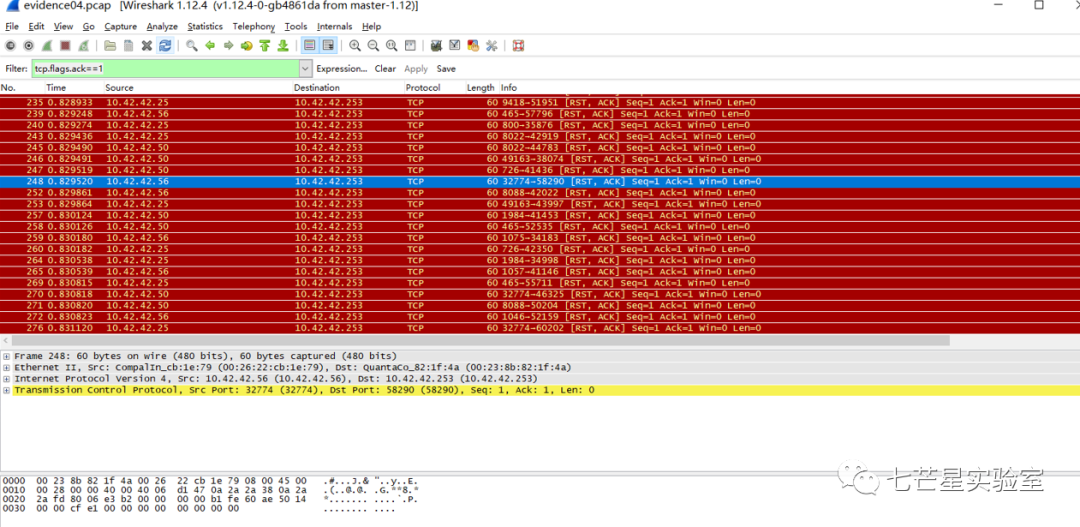
Identify IP addresses 10.42.42.50, 10.42.42.25, 10.42.42.56
Next, we resolve the fourth question—What is the MAC address of the Apple system he found? We can see this in Wireshark by locating the apple label in the static-endpoint.
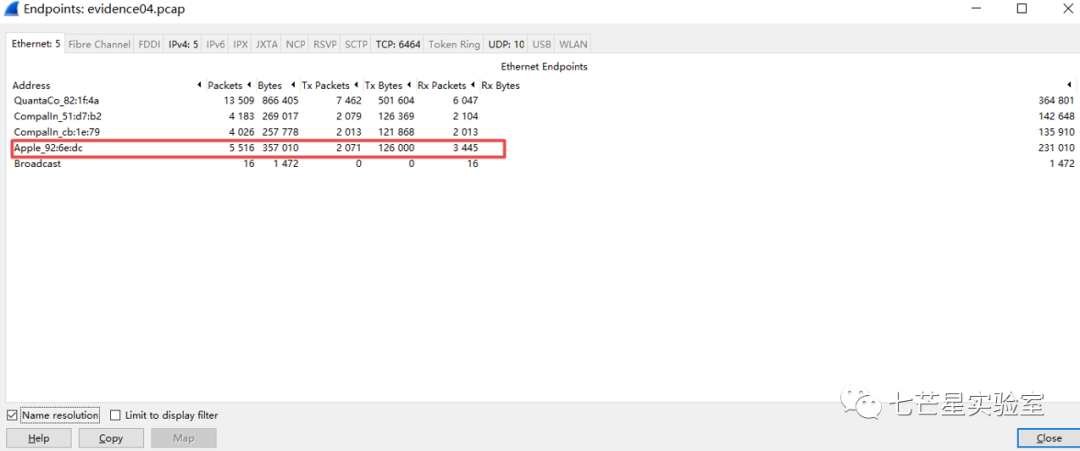
Then uncheck the “Name resolution” option to obtain the MAC address—00:16:cb:92:6e:dc
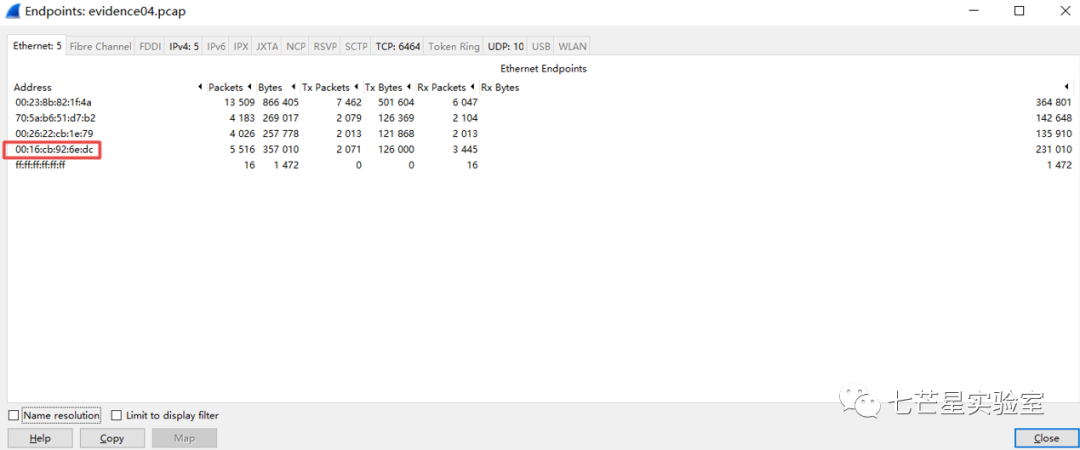
Next, we address the fifth question—what is the IP address of the Windows system he found. Here, we should note that Linux and Windows have different TTL values, which can be used as a distinguishing factor.
So, we can filter directly, and all source IPs will be 10.42.42.50.
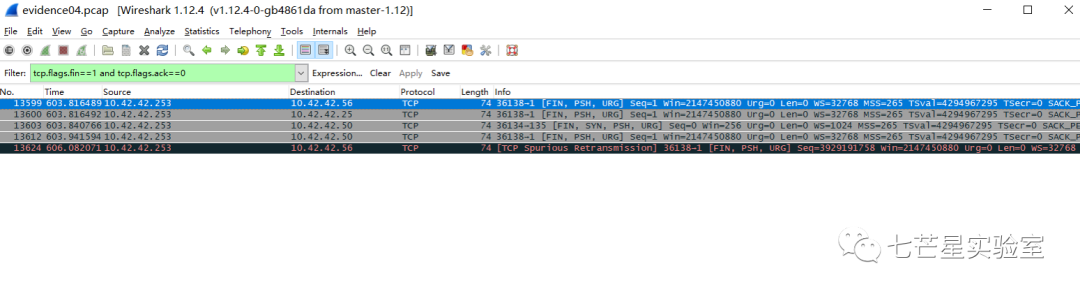
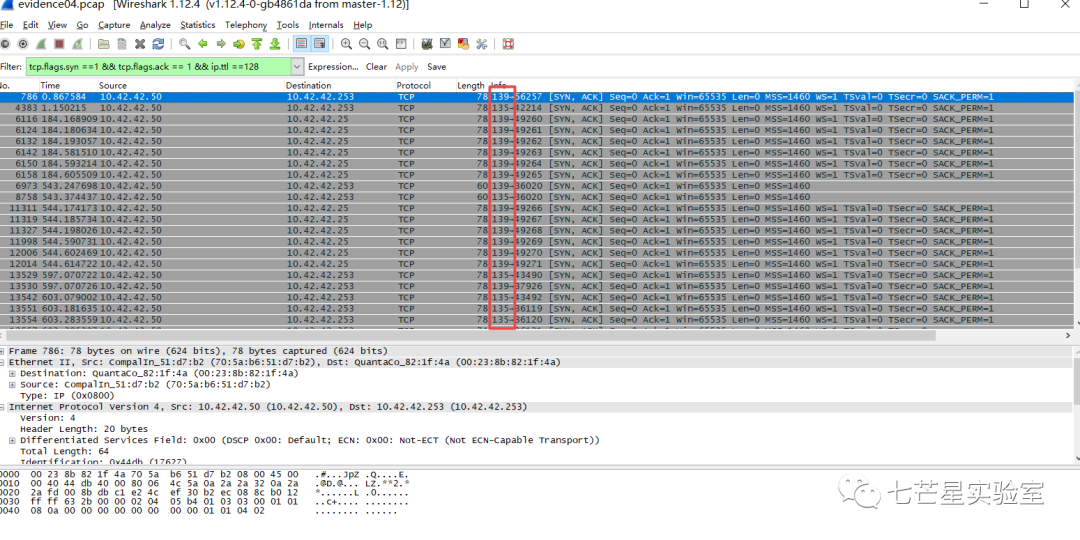
The remaining task is the last question—the TCP ports open on the Windows system? (List in decimal from lowest to highest). We can use the following query to see only port numbers 139 and 135.
This article provides a simple introduction to the function options and port scanning attack identification in Wireshark through packet analysis, along with supplementary explanations on distinguishing platforms between Windows and Linux.