I. What is the URL accessed by the malicious program to get the zip file?
Open the traffic packet with Wireshark, and check the files transferred over the HTTP protocol by going to File -> Export Objects -> HTTP.
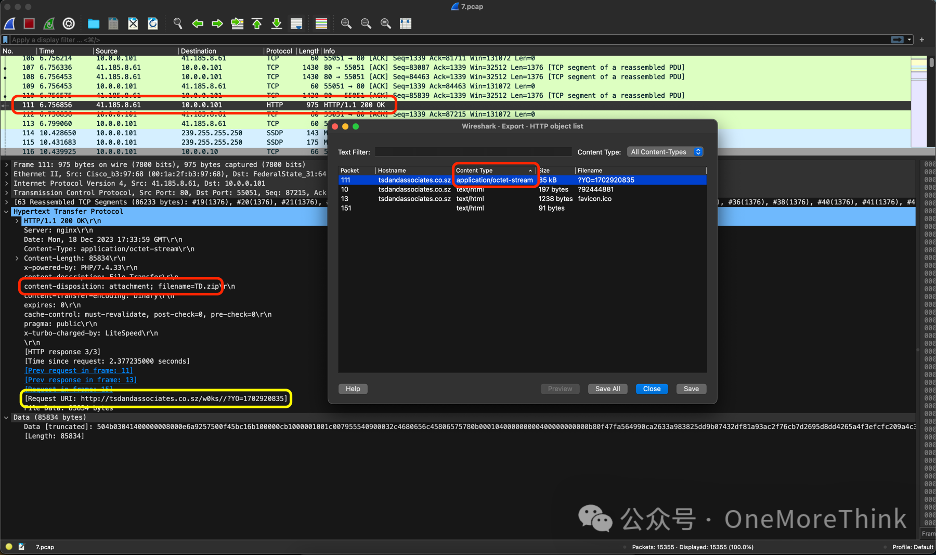
Select the file with Content Type as application/octet-stream. Wireshark will automatically locate the corresponding request. In the request details, you can see that the file being transferred is TD.zip, and the request URI is http://tsdandassociates.co.sz/w0ks//?YO=1702920835.
flag{tsdandassociates.co.sz/w0ks//?YO=1702920835}
II. What is the MD5 of the acquired zip file?
In File -> Export Objects -> HTTP, select Save All to download all files transferred over the HTTP protocol.
Use the command md5sum %3fYO=1702920835 to obtain the MD5 value of the zip file.
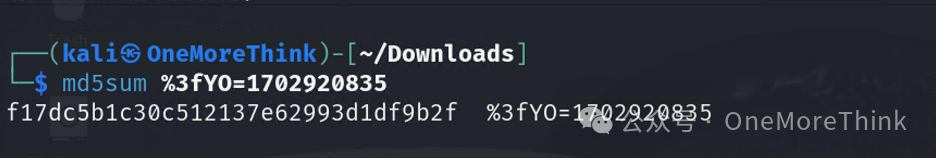
flag{f17dc5b1c30c512137e62993d1df9b2f}
III. After extracting the zip file, it downloads further malicious programs by loading a JavaScript file to another domain. What is that domain?
Unzip the archive to obtain two files: Nuj.js and y.
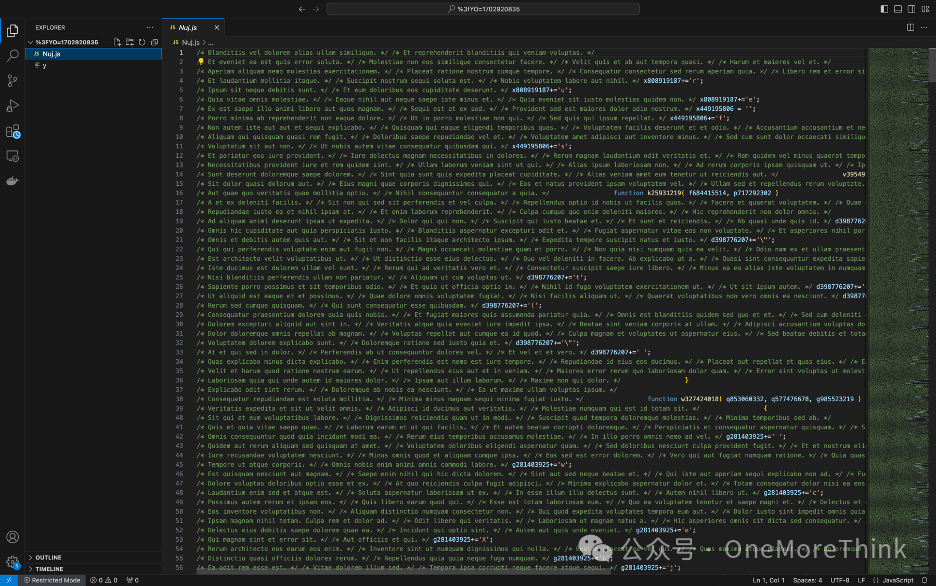
The JavaScript file contains extensive comments. Use an online JS de-commenting tool (https://www.sojson.com/jsjiemi.html) to remove the comments.
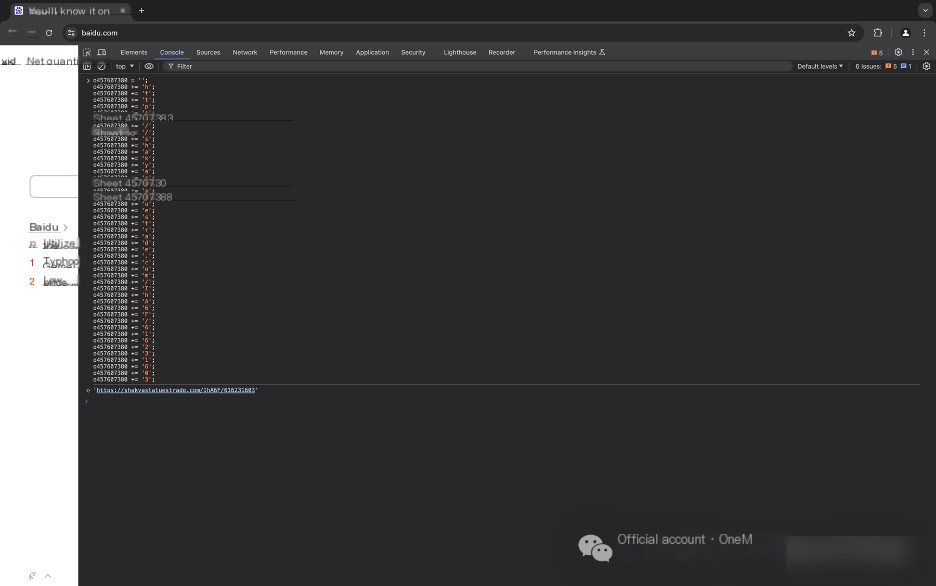
After removing comments from the JavaScript, it becomes evident that a certain variable is a URL address.
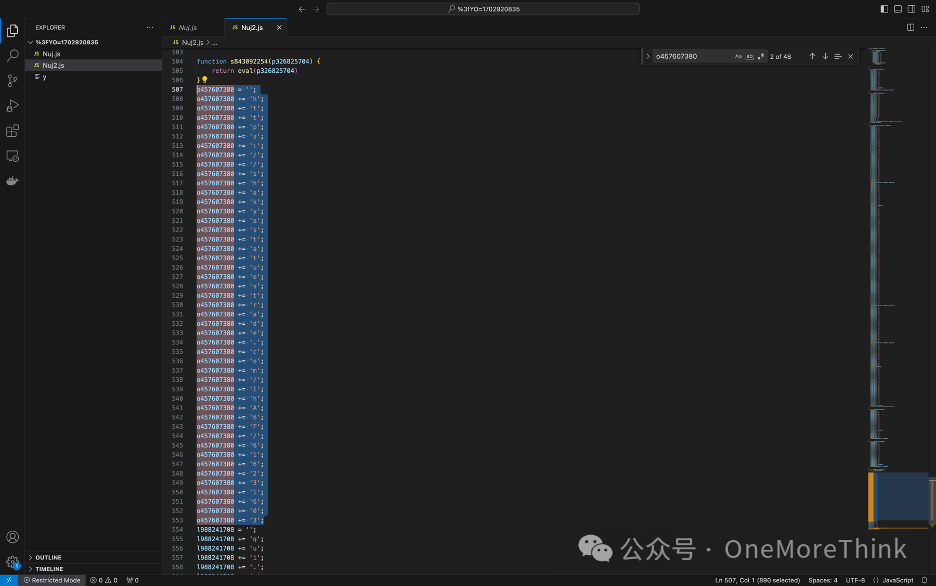
Execute the relevant code in the browser’s console to obtain the variable’s value: https://shakyastatuestrade.com/IhA6F/616231603.