Hello, this is the Digital World Network Technology Alliance Station.
In today’s digital world, networks have become an indispensable part of our daily lives and business activities. Different types of networks connect devices and users on various scales, meeting a range of communication needs. This article will explore the five main types of networks: Local Area Network (LAN), Metropolitan Area Network (MAN), Wide Area Network (WAN), Personal Area Network (PAN), and Wireless Network. Let’s get started!
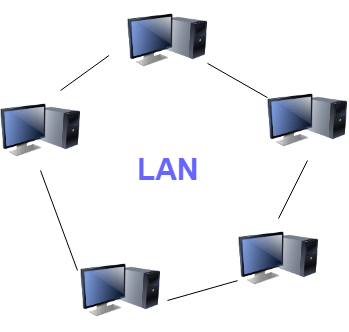
Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN (Local Area Network) is a network that covers a smaller geographic area. LANs are typically used to connect devices located in the same building or relatively close locations.
Characteristics of the Digital World
- Limited Range: LANs usually cover a relatively small area, such as homes, offices, and schools.
- High-Speed Connectivity: LANs offer high-speed data transmission, typically at gigabit speeds or higher.
- Common Topologies: LANs can use star, bus, or ring topologies.
Applications in the Digital World
- Office Networks: Used for connecting computers, printers, and servers within an office.
- Home Networks: Used for connecting multiple devices at home, such as smartphones, tablets, and smart TVs.
- School Networks: Used for educational and administrative purposes in schools, supporting teaching and online learning for students.
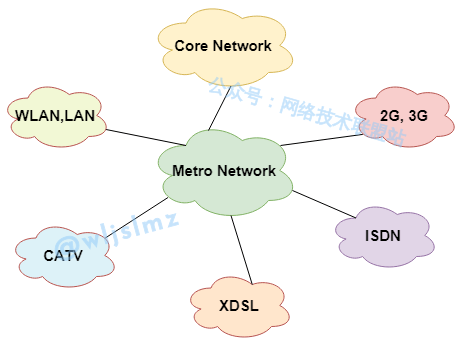
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) covers a larger geographic area than a LAN, usually encompassing a whole city or city regions.
Characteristics of the Digital World
- Moderate Range: The coverage of a MAN is larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN.
- Citywide Reach: Typically used to connect organizations or institutions across different city areas.
- Diverse Connection Technologies: MANs can use various technologies including fiber optics and wireless connections.
“Applications in the Digital World”
- City Government: Used for communication and data sharing between city government departments.
- Healthcare: Connects different healthcare institutions to enable medical data sharing and telemedicine services.
- Financial Institutions: Used for rapid data transmission between banks and financial companies.
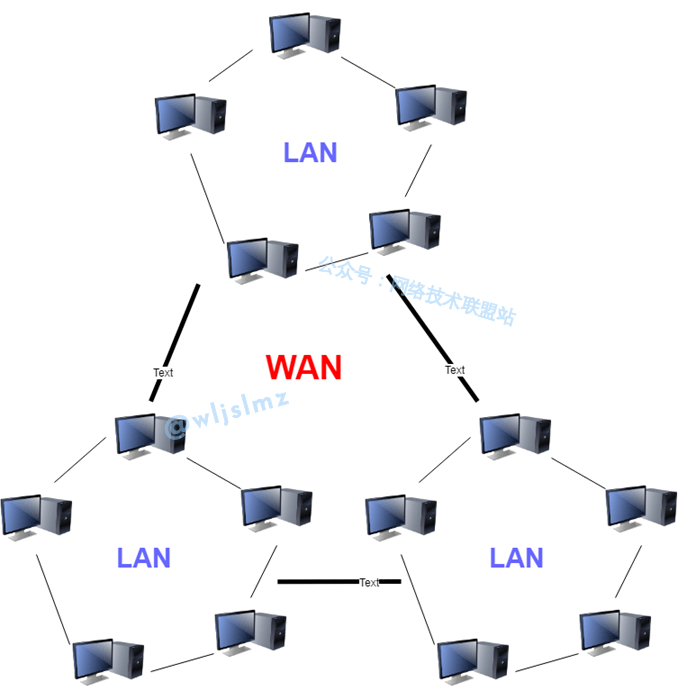
Wide Area Network (WAN)
WAN (Wide Area Network) spans a larger geographic area, often connecting devices in different cities, countries, or continents.
Characteristics of the Digital World
- Extensive Range: WANs have a very extensive range and can connect distant locations.
- Multiple Transmission Media: WANs can utilize various transmission media, including telephone lines, fiber optics, satellite, and wireless communication.
- Part of the Internet: The Internet is the world’s largest WAN.
Applications in the Digital World
- Enterprise Networks: Used to connect different branches of multinational companies, enabling data sharing and remote work.
- Cloud Computing: Access to cloud services such as cloud storage and applications across WANs.
- Remote Education: Used for online education, remote training, and e-learning.
Personal Area Network (PAN)
PAN (Personal Area Network) is the smallest range of network types, typically covering only personal device connections.
Characteristics of the Digital World
- Very Small Range: PANs cover a very small range, usually no more than a few meters.
- Personal Device Connections: Used to connect personal devices like smartphones, headphones, and smartwatches.
- Bluetooth Technology: Bluetooth is a common PAN connection technology.
Applications in the Digital World
- Wireless Headphones: Used to connect headphones to a smartphone or other audio source.
- Smart Homes: Used to connect smart home devices such as smart lights, smart locks, and smart thermostats.
- Medical Devices: Used to connect patient monitoring devices and medical sensors.
Wireless Network
Wireless networks are a type of network communication that uses wireless signals and are widely used in various fields.
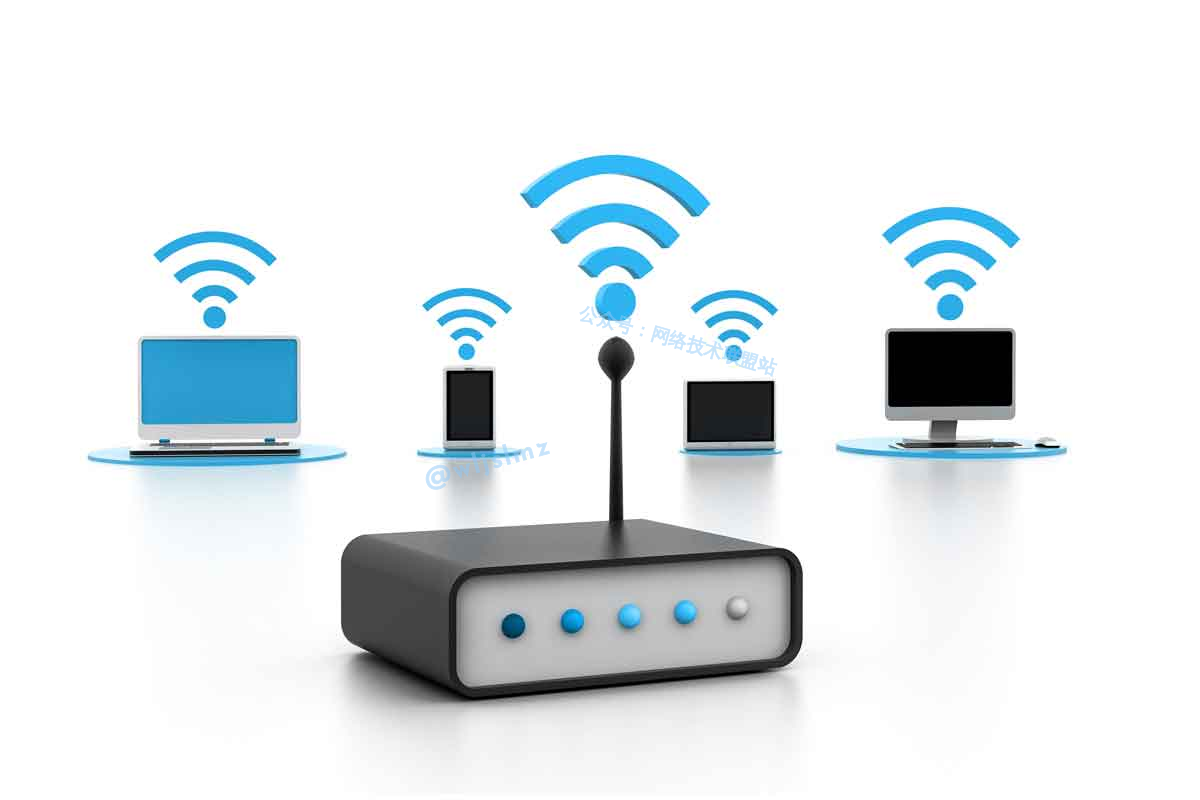

Characteristics of the Digital World
- Wireless Connection: Communication occurs without physical cables, using radio frequency signals.
- Mobility: Wireless networks allow devices to move within the coverage area, such as Wi-Fi and mobile cellular communication.
- Multiple Standards: There are multiple wireless communication standards, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 4G, and 5G.
Applications in the Digital World
- Wi-Fi Networks: Used in homes, offices, cafés, etc., providing wireless internet access.
- Mobile Communication: Enabled through 4G and 5G networks for mobile calls, SMS, and mobile data transfer.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Used for connecting various IoT devices such as smart homes, smart cities, and smart factory equipment.
Conclusion
Different types of networks connect devices and users at different scales to meet various communication needs. From the LAN covering smaller geographical areas to WAN that spans cities and countries, to PAN connecting personal devices and wireless networks using radio signals, network technology continues to evolve, providing convenience and connectivity to our lives and work. In the future, with the continuous emergence of new technologies, networks will continue to develop to satisfy the growing communication demands.
For example:
- 5G Technology: 5G networks will offer higher bandwidth and lower latency, supporting more IoT devices and faster mobile communications.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing will process data at the network edge, reducing latency and suitable for real-time applications and IoT devices.
- Quantum Communication: Quantum communication will offer higher levels of security, preventing data from being hacked, especially for military and sensitive data transmission.
- Satellite Internet: Several companies are planning to use satellites to provide global internet access, enhancing network coverage in remote areas.