1. Overview of Snort
Snort is a powerful network intrusion detection/prevention system, or NIDS/NIPS, featuring multi-platform, real-time traffic analysis, and network IP data packet logging capabilities.
1.1. Operating Modes
Snort operates in three modes: sniffer, packet logger, and network intrusion detection system.
1. Sniffer: The sniffer mode only reads packets from the network and displays them continuously in the terminal. 2. Packet Logger: The packet logger mode saves the packets to the hard drive. 3. Network Intrusion Detection: The network intrusion detection mode is the most complex and configurable. We can configure Snort to analyze network traffic to match user-defined rules and take actions based on the detection results.
When using Snort, the network card is automatically set to promiscuous mode
2. Snort Installation and Download
For 32-bit systems, WinpCap must be installed when using Snort.
Snort download link: https://www.snort.org/downloads#snort-downloads  WinpCap download link: https://www.winpcap.org/install/default.htm
WinpCap download link: https://www.winpcap.org/install/default.htm 
 Simply install it (for the convenience of subsequent experiments, it is strongly recommended to install in the root directory of the C drive)
Simply install it (for the convenience of subsequent experiments, it is strongly recommended to install in the root directory of the C drive) 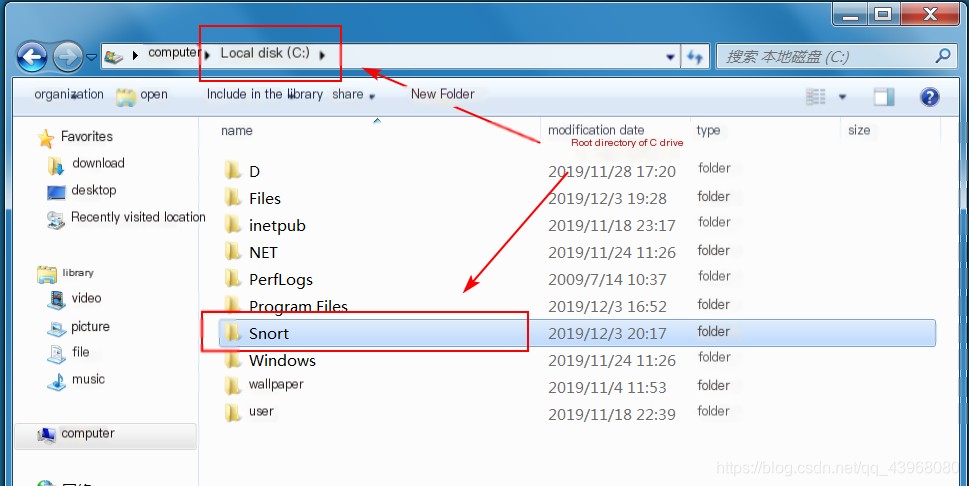
3. Sniffing and Data Logging
3.1. Sniffing
Open cmd in the Snort bin directory 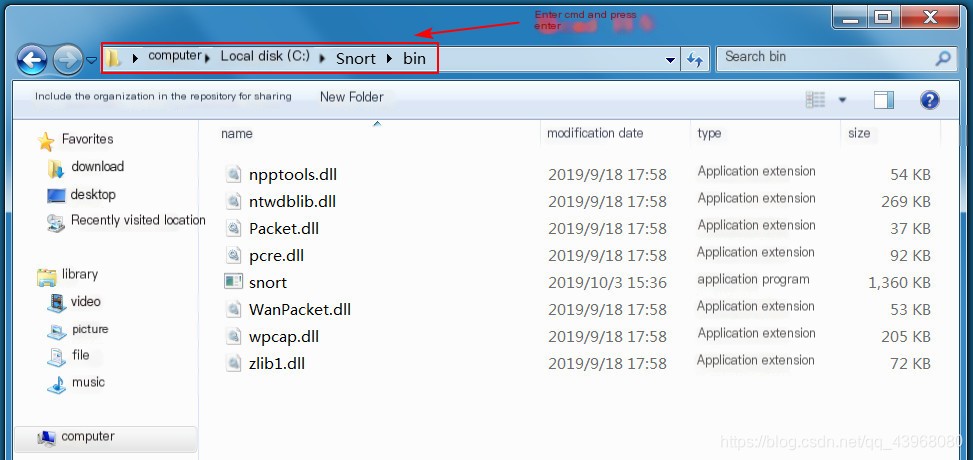 Enter snort -W to view the current network card
Enter snort -W to view the current network card 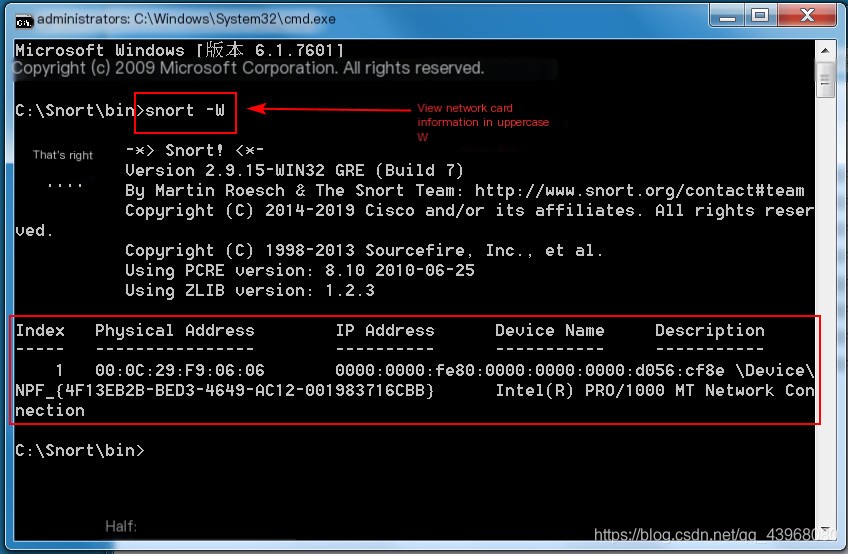 Sniff network card 1: Snort -v -i1
Sniff network card 1: Snort -v -i1 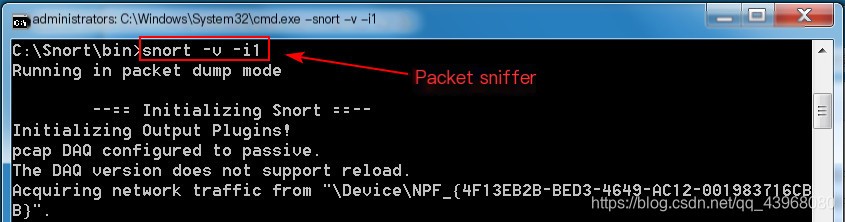 Ping this host from another machine
Ping this host from another machine  Packets are already being displayed
Packets are already being displayed 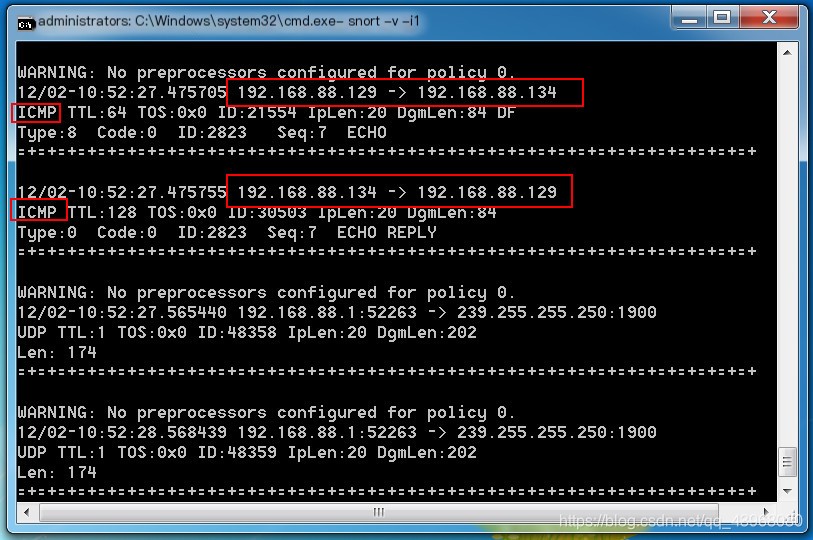 After stopping with ctrl + c, you can view packet analysis
After stopping with ctrl + c, you can view packet analysis 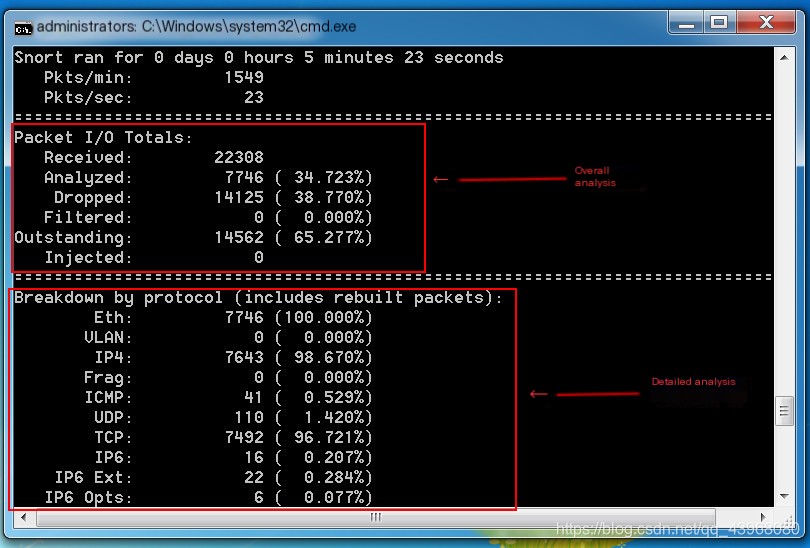
3.2. Data Packet Logging
The Snort directory has a default log folder, and logs can be saved directly to this folder  Use Snort -dve -i1 -h 192.168.88.0/24 -l c:\Snort\log -K ascii to log packets, where
Use Snort -dve -i1 -h 192.168.88.0/24 -l c:\Snort\log -K ascii to log packets, where
-dve means verbose sniffing mode -h specifies the host segment being monitored, unspecified it defaults to the local IP -l specifies the log location -K specifies the character set, stored in ASCII
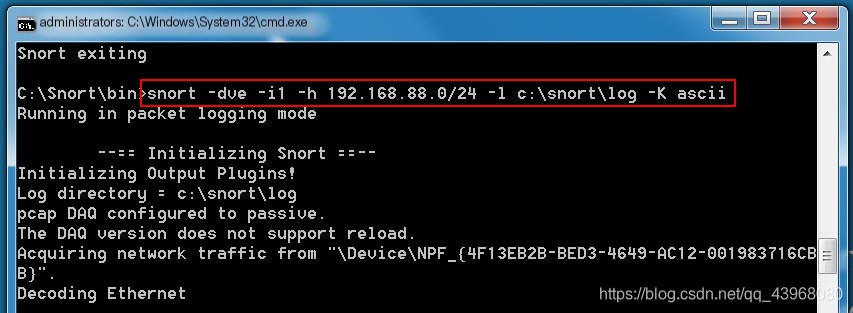 Access any webpage to see captured packet results
Access any webpage to see captured packet results 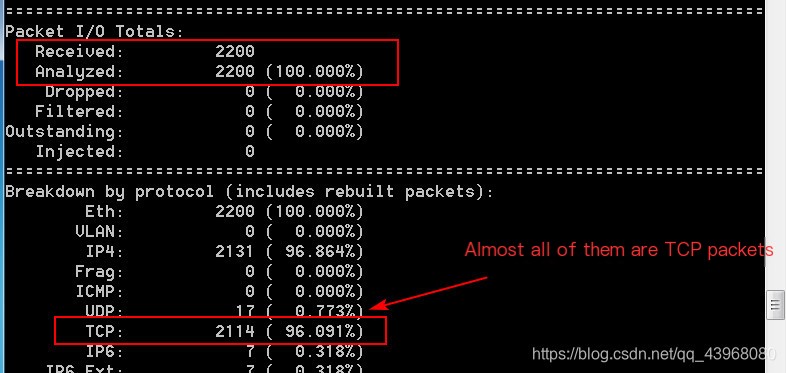
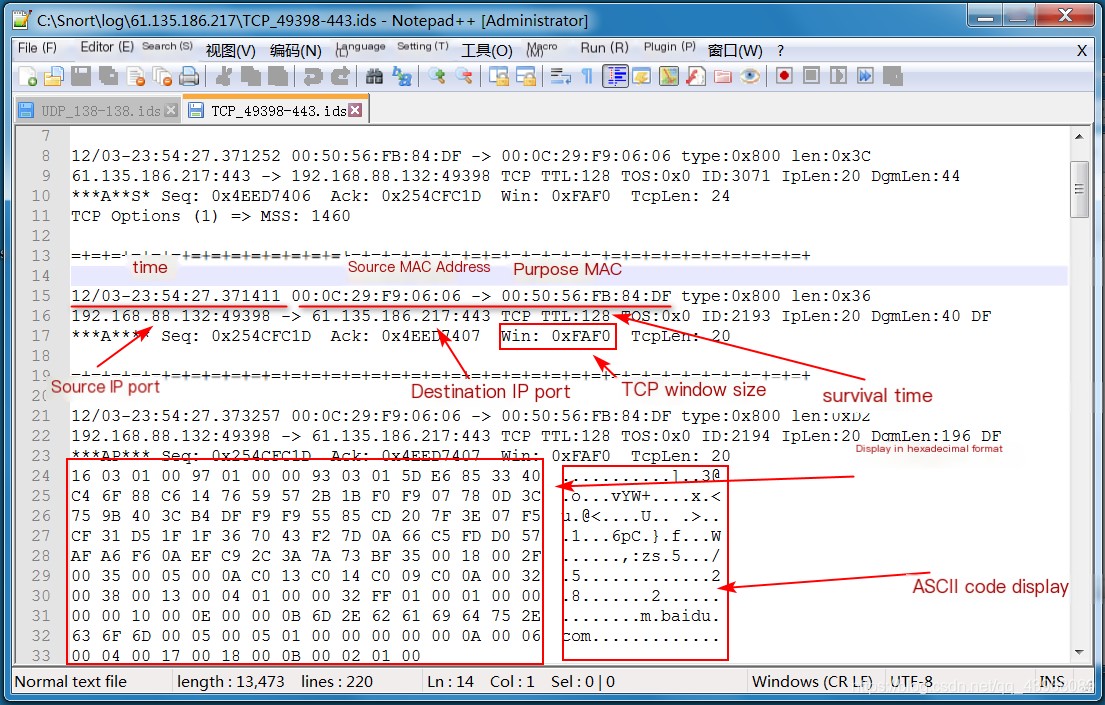
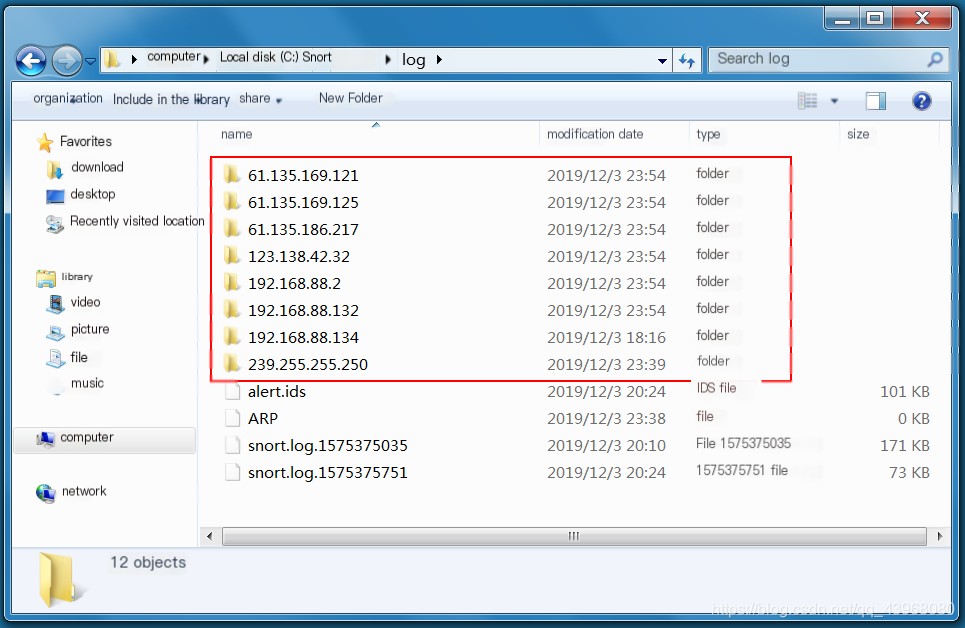 View the file content to see the data header
View the file content to see the data header