Introduction
In daily network maintenance, effective troubleshooting is essential to ensure smooth network operations. Basic network troubleshooting provides a comprehensive set of solutions and steps to quickly identify the source of issues and take appropriate corrective measures. This article outlines various troubleshooting strategies for different types of network issues, common methods, and case studies to help network administrators efficiently address a range of network problems.
1. Basic Network Troubleshooting Ideas
1.1 Locating fault range
① Network-wide network failure: The source of the failure can be located at the exit or core area;
②Small-scale network failure: The fault source can be located in the corresponding device or link closest to the fault source;
③Single-point network failure: The source of the failure can be located at the failure source itself.
1.2 Basic Network Troubleshooting
① The overall idea is “link” à “configuration”.
②First, confirm whether there are any human changes in the network or related equipment;
③ Secondly, check whether the physical link and equipment are normal;
④Finally, check the relevant properties or configurations of the network device.
2. Common Basic Network Troubleshooting Methods
2.1 Network equipment
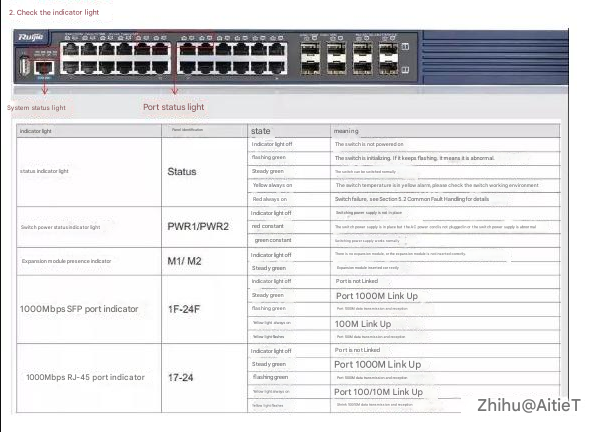
① Check the status lights, including the power indicator, status light, and alarm light;
② Sense the temperature of the device and check whether the temperature is too high.
2.2 Physical link
① Check the link indicator light;
② Plug and unplug the link; (Note: It is not recommended to plug and unplug the optical fiber link multiple times, and the multi-mode optical fiber can be seen by the naked eye)
③Change the port.
2.3 Terminal host
The following common commands can be used in the Windows system
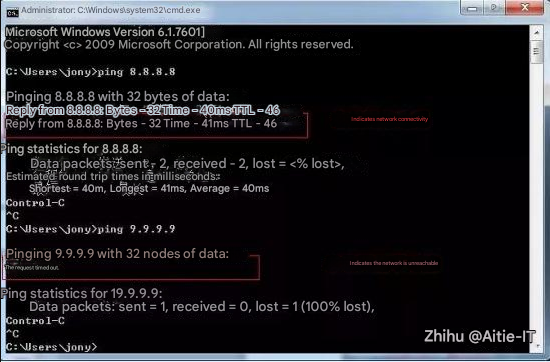
ping 192.168.100.254 !Connectivity test
tracert –d 192.168.10.254 !Path tracing
ipconfig /all ! Check network card information
ipconfig /release ! Reset network card information
ipconfig /renew ! Re-obtain IP address (under DHCP environment)
ipconfig /flushdns !Flush DNS cache
arp –a ! View ARP information
arp -d ! Reset network card ARP information
telnet 192.168.100.254 !Remote login
Test whether the network is unobstructed.
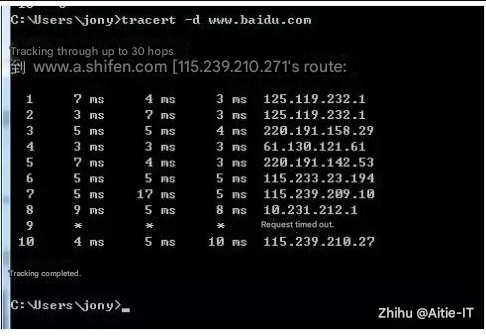
2.4 Segment positioning
From the user’s PC to the access switch.
From access switches to aggregation switches.
From aggregation layer switches to core switches.
From core switches to firewalls.
From firewall to router.
From router to egress gateway.
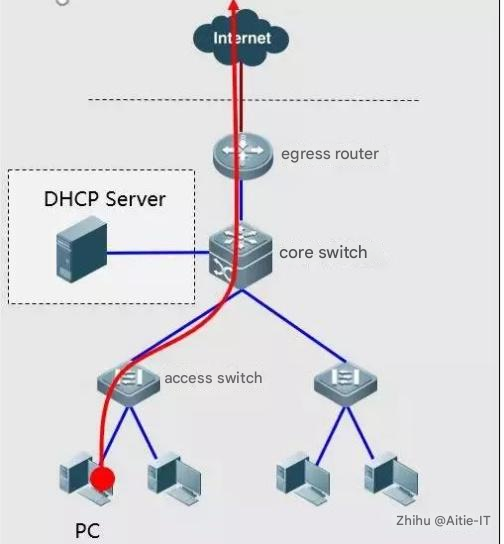
3. Basic Network Troubleshooting Through Network Device Usage and Indicator Light Viewing
3.1 Network usage environment
①Temperature requirement: 15℃~30℃
②Relative humidity requirement: 40%~65%
③ Cleanliness requirement: ≤ 1.3×105 (dust particle diameter ≥ 5μm)
④ Anti-interference requirements: Stay away from high-power, high-frequency, and high-current equipment
⑤AC power supply requirements: 100-240V~/50-60Hz
⑥ Maintain good ventilation between equipment to prevent heat flashing
4. Basic Network Troubleshooting Collection: Failure Case
Basic Network Troubleshooting Case 1: PC cannot obtain the IP address
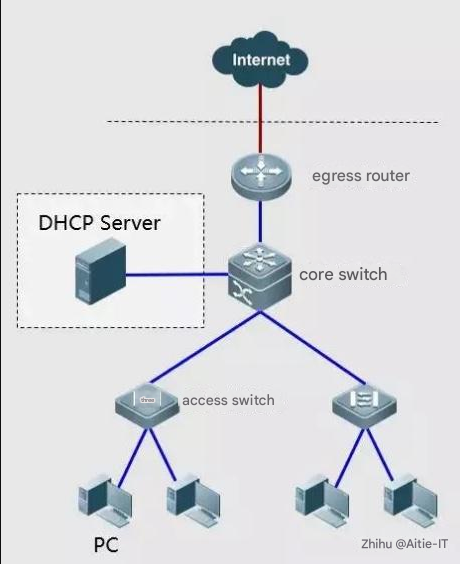
Troubleshooting steps:
① Check whether the DHCP server is normal and whether related services are running.
② Ping the DHCP server from the host and core switch respectively.
③After setting a static IP address on the intranet, check whether you can ping the gateway.
Based on the above results, check whether there is any fault from Link à Setup.
Basic Network Troubleshooting Case 2: The PC can obtain an IP address but cannot access the Internet
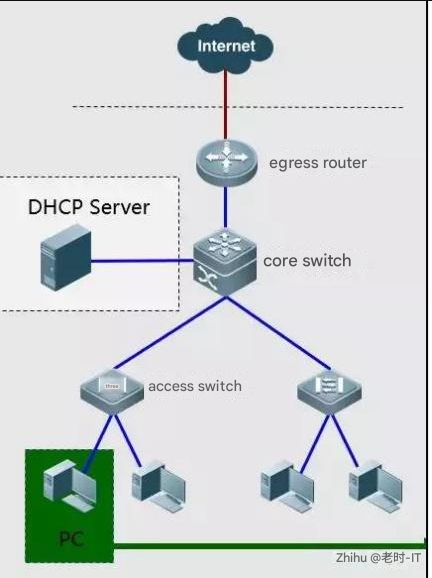
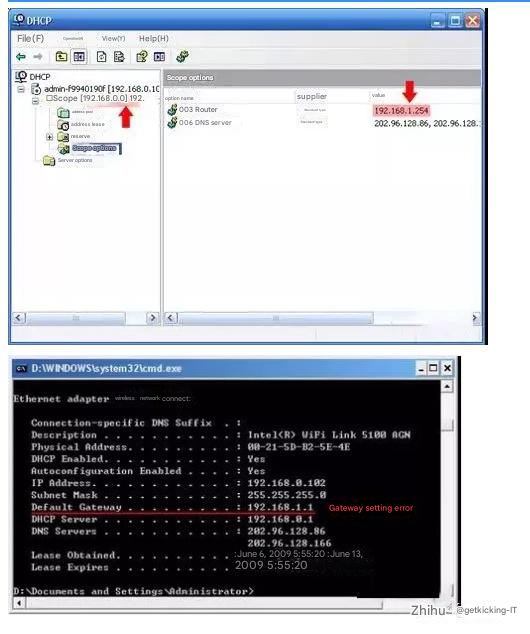
Troubleshooting steps: On the host that cannot access the Internet, run cmd—>ipconfig /all to check the IP address information obtained.
If the following figure appears, it means that the setting of the “003 default route” of the corresponding working domain of the DHCP server is incorrect.
Failure Case-3: PC obtains the wrong IP address
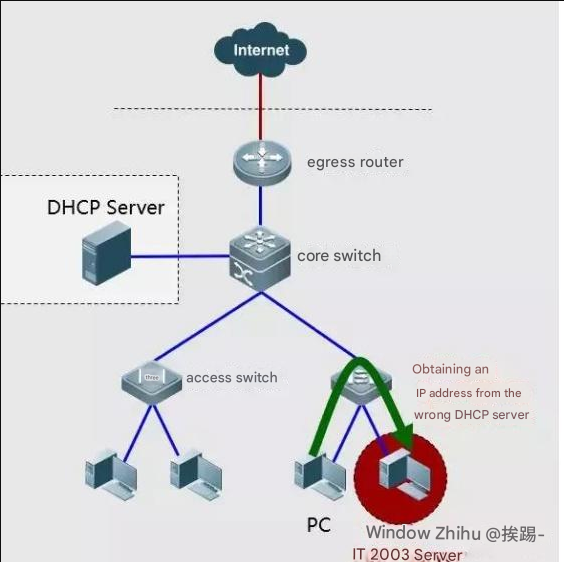
Troubleshooting steps:
Check whether anyone in the intranet uses Windows 2003 Server as the operating system and has enabled the DHCP service, or uses a wireless broadband router, which confuses address acquisition.
Solution: You can enable DHCP Snooping on the access switch, allowing DHCP offer messages to be obtained only from the trusted uplink port, but not from the downlink port.
Failure Case-4: PC cannot access the website via domain name
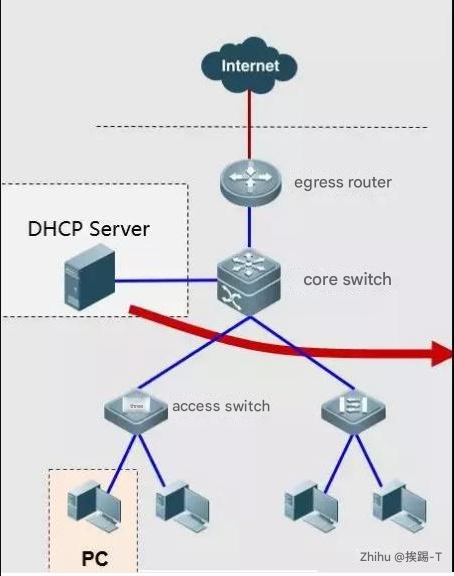
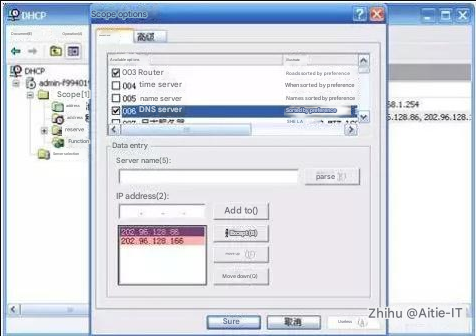
Troubleshooting steps: DNS is not set or is set incorrectly.
Basic Network Troubleshooting Case 5: ARP Spoofing Attack
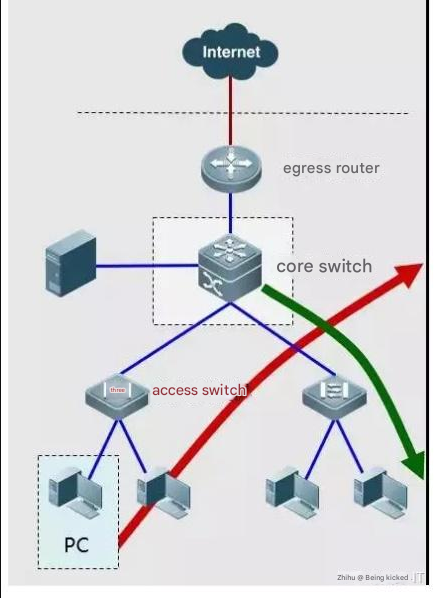
Troubleshooting steps: On the host that cannot access the Internet, run cmdàipconfig /all to check the IP address information obtained.
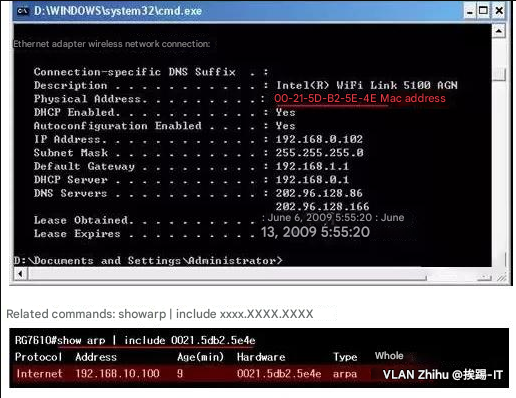
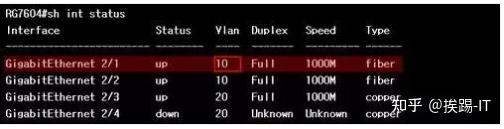
Fault Case-6: Configuration Error—Interface VLAN Division Error
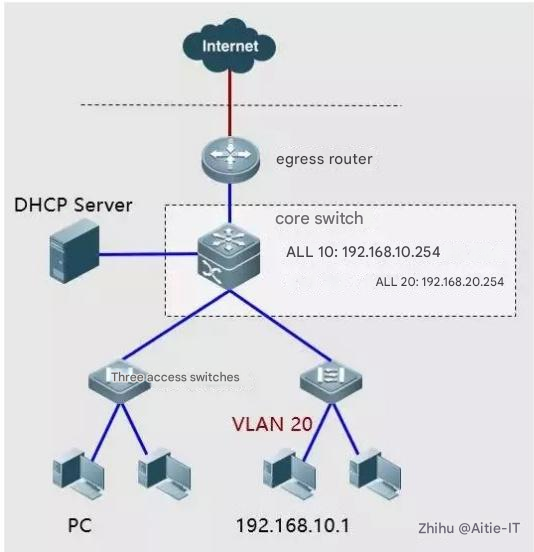
This mode usually appears in an environment where a static IP address is set.
Fault phenomenon: The host cannot ping the gateway.
Troubleshooting steps: cmdàipconfig /all to check the host IP address.
Check the VLAN settings of the corresponding ports on the switch.
Related command: show run
show int status
Basic Network Troubleshooting Case 7: Network Loop
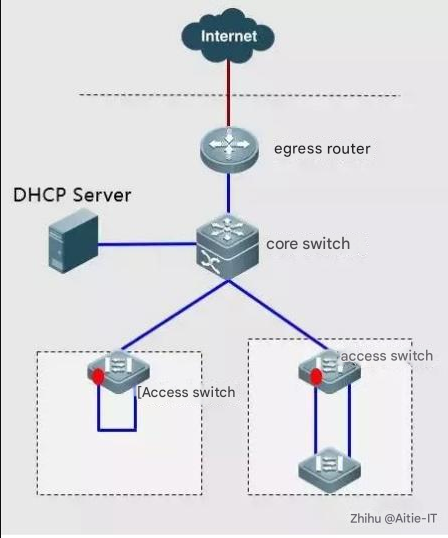
Phenomenon: The switch port indicators flash synchronously, the PC pings the external network and loses packets, and the Internet access is very slow
Troubleshooting method: Find the network cable or port that causes the loop by closing the port;
Solution: Enable a spanning tree to solve the problem. For the second method, enable spanning-tree bpduguard enable on the connected PC port.
Fault Case 8: Only some network segments in the school can access the Internet, and others are not allowed
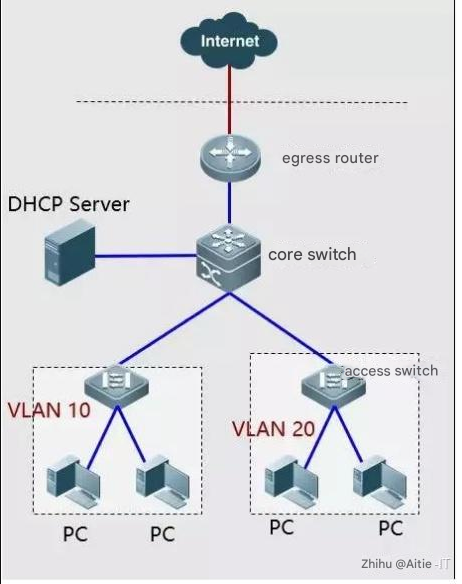
Phenomenon: Only some network segments within the campus network can access the Internet, while other network segments are not allowed
Troubleshooting methods: 1. Check whether there are any restrictions in the egress router list; 2. Check whether the router’s back-pointing route is normal;
Solution: 1. Modify NAT ACL; 2. Add a back-pointing route;
Failure Case-9: The intranet server cannot be accessed from the public network
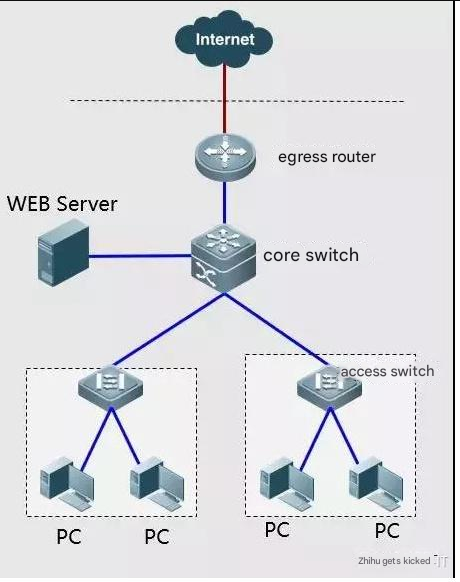
Phenomenon: The school’s WEB server cannot be accessed through the public network address outside the school;
Troubleshooting method: Check whether the egress router has port mapping;
Solution: Add port mapping to solve the problem.
Conclusion
Following basic network troubleshooting methods, network administrators can swiftly locate issues and take the necessary actions to restore normal network operations. Whether the problems involve devices, physical links, or terminal hosts, the troubleshooting steps and case analyses provided here offer practical guidance for efficiently resolving network issues. These methods help improve network management efficiency, delivering a more stable network experience for users.


